import numpy as npimport pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt%matplotlib inline
tennis = pd.read_csv('tennis.csv')tennis
outlooktemphumiditywindyplay
0sunnyhothighFalseno
1sunnyhothighTrueno
2overcasthothighFalseyes
3rainymildhighFalseyes
4rainycoolnormalFalseyes
5rainycoolnormalTrueno
6overcastcoolnormalTrueyes
7sunnymildhighFalseno
8sunnycoolnormalFalseyes
9rainymildnormalFalseyes
10sunnymildnormalTrueyes
11overcastmildhighTrueyes
12overcasthotnormalFalseyes
13rainymildhighTrueno
Lets take a look at how each category looks when inside a frequency table:
outlook = tennis.groupby(['outlook', 'play']).size()temp = tennis.groupby(['temp', 'play']).size()humidity = tennis.groupby(['humidity', 'play']).size()windy = tennis.groupby(['windy', 'play']).size()play = tennis.play.value_counts()
print(temp)print('------------------')print(humidity)print('------------------')print(windy)print('------------------')print(outlook)print('------------------')print('play')print(play)
temp playcool no 1 yes 3hot no 2 yes 2mild no 2 yes 4dtype: int64------------------humidity playhigh no 4 yes 3normal no 1 yes 6dtype: int64------------------windy playFalse no 2 yes 6True no 3 yes 3dtype: int64------------------outlook playovercast yes 4rainy no 2 yes 3sunny no 3 yes 2dtype: int64------------------playyes 9no 5Name: play, dtype: int64
What is the probability of playing tennis given it is rainy?
- P(rain|play=yes)
- frequency of (outlook=rainy) when (play=yes) / frequency of (play=yes) = 3/9
- P(play=yes)
- frequency of (play=yes) / total(play) = 9/14
- P(outlook=rainy)
- frequency of (outlook=rainy) / total(outlook) = 5/14

(3/9)*(9/14)/(5/14)
0.6
The probability of playing tennis when it is rainy is 60%. The process is very simple once you obtain the frequencies for each category.
Here is a simple function to help any newbies remember the parts of Bayes equation:
def bayestheorem(): print('Posterior [P(c|x)] - Posterior probability of the target/class (c) given predictors (x)'), print('Prior [P(c)] - Prior probability of the class (target)'), print('Likelihood [P(x|c)] - Probability of the predictor (x) given the class/target (c)'), print('Evidence [P(x)] - Prior probability of the predictor (x))')
Here is a simple function to calculate the posterior probability for you, but you must be able to find each part of bayes equation yourself.
def bayesposterior(prior, likelihood, evidence, string): print('Prior=', prior), print('Likelihood=', likelihood), print('Evidence=', evidence), print('Equation =','(Prior*Likelihood)/Evidence') print(string, (prior*likelihood)/evidence)
Lets see another way to find the posterior probability this time using contingency tables in Python:
ct = pd.crosstab(tennis['outlook'], tennis['play'], margins = True)print(ct)
no yes rowtotalovercast 0 4 4rainy 2 3 5sunny 3 2 5coltotal 5 9 14
ct.columns = ["no","yes","rowtotal"]ct.index= ["overcast","rainy","sunny","coltotal"]ct / ct.loc["coltotal","rowtotal"]
noyesrowtotal
overcast0.0000000.2857140.285714
rainy0.1428570.2142860.357143
sunny0.2142860.1428570.357143
coltotal0.3571430.6428571.000000
To only get the column total
ct / ct.loc["coltotal"]
noyesrowtotal
overcast0.00.4444440.285714
rainy0.40.3333330.357143
sunny0.60.2222220.357143
coltotal1.01.0000001.000000
To only get the row total
ct.div(ct["rowtotal"], axis=0)
noyesrowtotal
overcast0.0000001.0000001.0
rainy0.4000000.6000001.0
sunny0.6000000.4000001.0
coltotal0.3571430.6428571.0
These tables are all pandas dataframe objects. Therefore using pandas subsetting and the bayesposterior function I made, we can arrive at the same conclusion:
bayesposterior(prior = ct.iloc[1,1]/ct.iloc[3,1], likelihood = ct.iloc[3,1]/ct.iloc[3,2], evidence = ct.iloc[1,2]/ct.iloc[3,2], string = 'Probability of Tennis given Rain =')
Prior= 0.3333333333333333Likelihood= 0.6428571428571429Evidence= 0.35714285714285715Equation = (Prior*Likelihood)/EvidenceProbability of Tennis given Rain = 0.6
Naive Bayes Algorithm
Naive Bayes is a supervised Machine Learning algorithm inspired by the Bayes theorem. It works on the principles of conditional probability. Naive Bayes is a classification algorithm for binary and multi-class classification. The Naive Bayes algorithm uses the probabilities of each attribute belonging to each class to make a prediction.
Example
What is the probability of playing tennis when it is sunny, hot, highly humid and windy? So using the tennis dataset, we need to use the Naive Bayes method to predict the probability of someone playing tennis given the mentioned weather conditions.
pd.crosstab(tennis['outlook'], tennis['play'], margins = True)
playnoyesAll
outlook
overcast044
rainy235
sunny325
All5914
pd.crosstab(tennis['temp'], tennis['play'], margins = True)
playnoyesAll
temp
cool134
hot224
mild246
All5914
pd.crosstab(tennis['humidity'], tennis['play'], margins = True)
playnoyesAll
humidity
high437
normal167
All5914
pd.crosstab(tennis['windy'], tennis['play'], margins = True)
playnoyesAll
windy
False268
True336
All5914
pd.crosstab(index=tennis['play'],columns="count", margins=True)
col_0countAll
play
no55
yes99
All1414
Now by using the above contingency tables, we will go through how the Naive Bayes algorithm calculates the posterior probability.
- Calculate P(x|play=yes). In this case x refers to all the predictors 'outlook', 'temp', 'humidity' and 'windy'.
- P(sunny|play=yes)→2/9
- P(hot|play=yes)→2/9
- P(high|play=yes)→3/9
- P(True|play=yes)→3/9
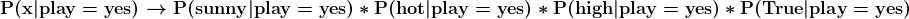
p_x_yes = ((2/9)*(2/9)*(3/9)*(3/9))print('The probability of the predictors given playing tennis is', '%.3f'%p_x_yes)
The probability of the predictors given playing tennis is 0.005 - Calculate P(x|play=no) using the same method as above.
- P(sunny|play=no)→3/5
- P(hot|play=no)→2/5
- P(high|play=no)→4/5
- P(True|play=no)→3/5
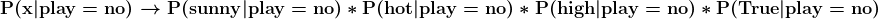
p_x_no = ((3/5)*(2/5)*(4/5)*(3/5))print('The probability of the predictors given not playing tennis is ', '%.3f'%p_x_no)
The probability of the predictors given not playing tennis is 0.115 - Calculate P(play=yes) and P(play=no)
- P(play=yes)→9/14
- P(play=yes)→5/14
yes = (9/14)no = (5/14)print('The probability of playing tennis is', '%.3f'% yes)print('The probability of not playing tennis is', '%.3f'% no)
The probability of playing tennis is 0.643The probability of not playing tennis is 0.357








 雷达卡
雷达卡
















 提升卡
提升卡 置顶卡
置顶卡 沉默卡
沉默卡 变色卡
变色卡 抢沙发
抢沙发 千斤顶
千斤顶 显身卡
显身卡


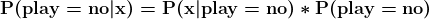







 京公网安备 11010802022788号
京公网安备 11010802022788号







