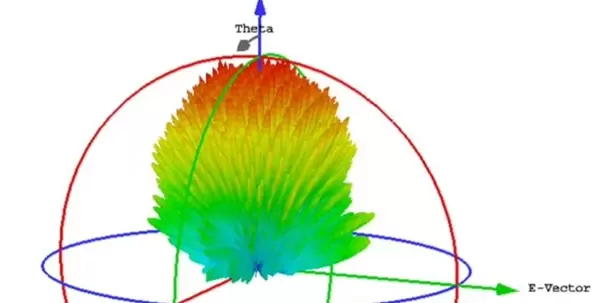
在天线与雷达隐身技术的研究中,编码超表面的雷达散射截面积(RCS)缩减已成为一个关键方向。通过引入遗传算法对编码序列进行优化,可显著提升漫反射性能,从而有效降低目标被探测的概率。该方法兼容多种位数(如1bit、2bit、3bit等)及不同规模(如6×6、8×8等)的编码阵列设计,并具备对单元相位偏差的容差能力,增强了工程实现的可行性。
利用MATLAB或Python编写相应代码,能够快速完成编码序列的优化过程,并自动生成远场分布结果。通过叠加公式计算远场波形,可直观观察优化后的电磁响应特性。同时,结合CST仿真软件,可以进一步验证超表面在实际电磁环境下的RCS缩减效果。
遗传算法的基本原理
遗传算法是一种模拟生物进化机制的全局优化方法,基于选择、交叉和变异操作,在迭代过程中不断筛选出适应度更高的个体。在此应用中,每个个体代表一种可能的编码序列,而适应度函数则依据其对应的RCS表现或漫反射均匀性来定义——RCS越低,适应度越高,优化目标即为寻找最优编码排布。
MATLAB中的实现流程
编码序列初始化
使用MATLAB生成初始种群,通常设定种群大小为50,每个个体为6×6尺寸的2bit编码矩阵。通过随机整数生成函数,确保每个元素落在0到2^num_bits - 1范围内,完成多样化的初始布局构建。
% 以6*6的2bit编码序列为例
num_rows = 6;
num_cols = 6;
num_bits = 2;
pop_size = 50; % 种群大小
population = randi([0, 2^num_bits - 1], [num_rows, num_cols, pop_size]);randi适应度评估
定义calculate_fitness函数用于量化每个个体的性能表现。遍历当前种群,调用预设的RCS计算模块(需用户自定义,示例中已简化处理),获取对应电磁响应值,并以RCS的倒数作为适应度指标——数值越大表示性能越优。
function fitness = calculate_fitness(population)
% 这里假设我们有一个计算RCS的函数calculate_RCS
[num_rows, num_cols, pop_size] = size(population);
fitness = zeros(1, pop_size);
for i = 1:pop_size
individual = population(:, :, i);
fitness(i) = calculate_RCS(individual);
end
% 这里RCS越小,适应度越高,所以取倒数作为适应度
fitness = 1./ fitness;
endcalculateRCS遗传操作执行
包括三大核心步骤:
- 选择:依据适应度高低挑选优质父代个体;
- 交叉:随机选取交叉点,将两个父代的部分编码片段重组,生成新后代;
- 变异:按设定概率对某些编码位进行随机翻转,增加种群多样性。
% 选择操作
function selected_population = selection(population, fitness, num_parents)
[~, idx] = sort(fitness, 'descend');
selected_population = population(:, :, idx(1:num_parents));
end
% 交叉操作
function new_population = crossover(parents, num_offspring)
[num_rows, num_cols, num_parents] = size(parents);
new_population = zeros(num_rows, num_cols, num_offspring);
for i = 1:num_offspring
parent1_idx = randi(num_parents);
parent2_idx = randi(num_parents);
parent1 = parents(:, :, parent1_idx);
parent2 = parents(:, :, parent2_idx);
crossover_point = randi([1, num_rows - 1]);
new_population(1:crossover_point, :, i) = parent1(1:crossover_point, :);
new_population(crossover_point + 1:end, :, i) = parent2(crossover_point + 1:end, :);
end
end
% 变异操作
function mutated_population = mutation(population, mutation_rate)
[num_rows, num_cols, pop_size] = size(population);
mutated_population = population;
for i = 1:pop_size
for j = 1:num_rows
for k = 1:num_cols
if rand < mutation_rate
mutated_population(j, k, i) = randi([0, 2^num_bits - 1]);
end
end
end
end
end主循环与结果输出
设置最大进化代数,每一代依次执行适应度计算与遗传操作,持续追踪最优解的变化趋势。最终输出收敛后的最佳编码序列,可用于后续仿真分析。
num_generations = 100;
num_parents = 20;
mutation_rate = 0.01;
for generation = 1:num_generations
fitness = calculate_fitness(population);
parents = selection(population, fitness, num_parents);
offspring = crossover(parents, pop_size - num_parents);
new_population = mutation([parents, offspring], mutation_rate);
population = new_population;
end
best_individual_idx = find(fitness == max(fitness));
best_individual = population(:, :, best_individual_idx);Python中的实现方式
种群初始化
借助NumPy库完成编码矩阵的随机生成,结构与MATLAB一致,构建由多个6×6二维数组组成的种群,支持灵活调整位深度与阵列规模。
import numpy as np
num_rows = 6
num_cols = 6
num_bits = 2
pop_size = 50
population = np.random.randint(0, 2**num_bits, size=(num_rows, num_cols, pop_size))numpy适应度函数设计
Python版本同样采用RCS倒数作为适应度标准,调用外部仿真接口或近似模型获取个体性能数据,保持与MATLAB逻辑的一致性。
def calculate_fitness(population):
num_rows, num_cols, pop_size = population.shape
fitness = np.zeros(pop_size)
for i in range(pop_size):
individual = population[:, :, i]
# 假设calculate_RCS函数已定义
fitness[i] = calculate_RCS(individual)
fitness = 1 / fitness
return fitnesscalculate_RCS遗传算子实现
利用Python内置的random模块或NumPy实现选择、交叉与变异过程,操作方式与MATLAB相似,但语法更简洁,便于调试与扩展。
import random
def selection(population, fitness, num_parents):
sorted_idx = np.argsort(fitness)[::-1]
selected_population = population[:, :, sorted_idx[:num_parents]]
return selected_population
def crossover(parents, num_offspring):
num_rows, num_cols, num_parents = parents.shape
new_population = np.zeros((num_rows, num_cols, num_offspring))
for i in range(num_offspring):
parent1_idx = random.randint(0, num_parents - 1)
parent2_idx = random.randint(0, num_parents - 1)
parent1 = parents[:, :, parent1_idx]
parent2 = parents[:, :, parent2_idx]
crossover_point = random.randint(1, num_rows - 1)
new_population[0:crossover_point, :, i] = parent1[0:crossover_point, :]
new_population[crossover_point:, :, i] = parent2[crossover_point:, :]
return new_population
def mutation(population, mutation_rate):
num_rows, num_cols, pop_size = population.shape
mutated_population = population.copy()
for i in range(pop_size):
for j in range(num_rows):
for k in range(num_cols):
if random.random() < mutation_rate:
mutated_population[j, k, i] = random.randint(0, 2 ** num_bits - 1)
return mutated_populationrandom主循环结构
循环控制机制与MATLAB类似,逐代演化并记录每代最优个体,直至达到预设终止条件,输出最终优化结果。
num_generations = 100
num_parents = 20
mutation_rate = 0.01
for generation in range(num_generations):
fitness = calculate_fitness(population)
parents = selection(population, fitness, num_parents)
offspring = crossover(parents, pop_size - num_parents)
new_population = mutation(np.concatenate((parents, offspring), axis=2), mutation_rate)
population = new_population
best_individual_idx = np.argmax(fitness)
best_individual = population[:, :, best_individual_idx]远场仿真可视化代码
MATLAB绘图功能
使用MATLAB内置的三维绘图函数,如surf或专用电磁场可视化工具,绘制远场辐射模式的立体图像;同时调用二维绘图命令展示能量分布图,清晰呈现漫反射效果。
% 假设已经得到最佳编码序列best_individual
% 计算远场效果(这里假设已有计算远场的函数calculate_far_field)
far_field_result = calculate_far_field(best_individual);
% 三维仿真
figure;
surf(far_field_result);
title('三维远场效果');
xlabel('X方向');
ylabel('Y方向');
zlabel('幅度');
% 二维能量图
figure;
contourf(abs(far_field_result));
title('二维能量图');
xlabel('X方向');
ylabel('Y方向');surfcontourfPython绘图实现
借助Matplotlib与Mayavi等可视化库,Python同样可实现高质量的三维远场仿真图与二维能量分布图,图形风格可定制,适合科研报告与论文插图需求。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 假设已经得到最佳编码序列best_individual
# 计算远场效果(这里假设已有计算远场的函数calculate_far_field)
far_field_result = calculate_far_field(best_individual)
# 三维仿真
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
X, Y = np.meshgrid(np.arange(far_field_result.shape[0]), np.arange(far_field_result.shape[1]))
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, np.abs(far_field_result), cmap='viridis')
ax.set_title('三维远场效果')
ax.set_xlabel('X方向')
ax.set_ylabel('Y方向')
ax.set_zlabel('幅度')
# 二维能量图
plt.figure()
plt.contourf(np.abs(far_field_result), cmap='viridis')
plt.title('二维能量图')
plt.xlabel('X方向')
plt.ylabel('Y方向')
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()matplotlibCST中查看RCS缩减效果的操作步骤
模型建立: 在CST Studio Suite中搭建超表面几何结构,根据优化所得编码序列配置各个单元的状态,确保排列顺序与尺寸符合设计要求。
求解器设置: 选用合适的求解器类型(如时域求解器或频域求解器),设定工作频率范围、边界条件、激励源以及网格划分精度,保证仿真准确性。
结果分析: 仿真完成后,在后处理模块中提取RCS相关数据,绘制其随入射角度或频率变化的曲线图,直观对比优化前后RCS差异,验证缩减效果。
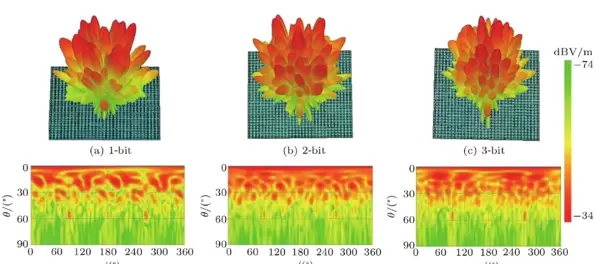
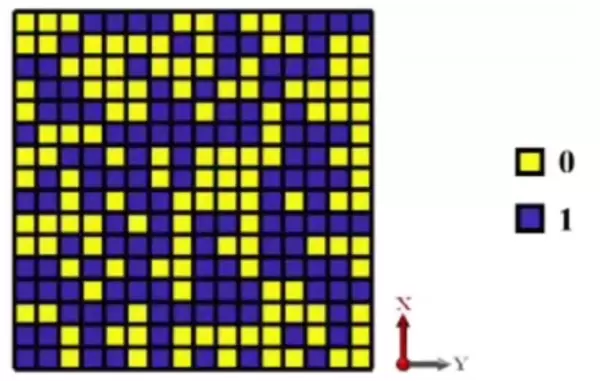
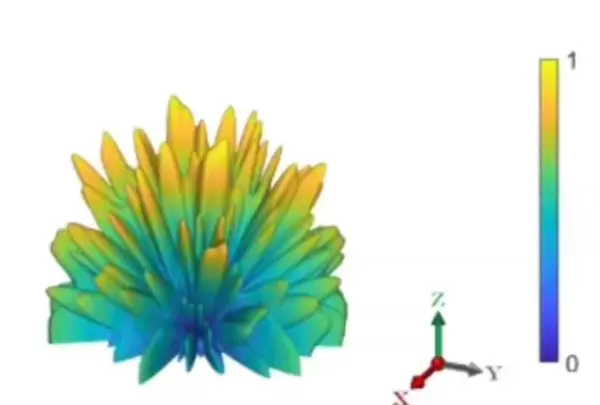

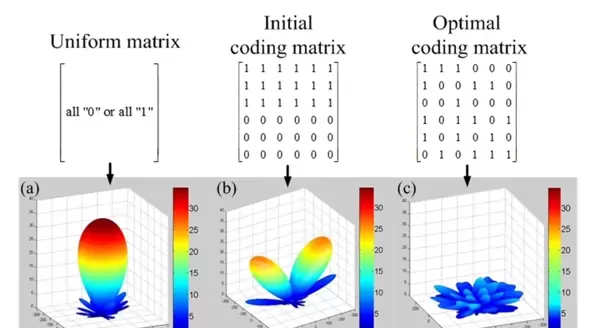
综上所述,通过遗传算法对编码序列进行智能优化,结合MATLAB与Python编程实现高效求解,再辅以CST的高精度电磁仿真,能够系统化地达成编码超表面的RCS抑制目标。该方案不仅适用于多种bit数和阵列规模,还考虑了实际加工中可能出现的相位误差,具备较强的鲁棒性和实用价值,在现代隐身技术和高性能天线设计中具有广阔的应用前景。




 雷达卡
雷达卡




 京公网安备 11010802022788号
京公网安备 11010802022788号







