CentOS 离线升级 OpenSSH 至 OpenSSH_9.9p1
漏洞背景说明
根据绿盟科技“远程安全评估系统”检测报告,当前 SSH 服务存在支持弱加密算法的安全风险(基于原理扫描发现)。为满足安全合规要求并彻底解决该问题,建议将 OpenSSH 升级至 9.0 或更高版本。具体实施方案需结合实际操作系统环境进行选择,尤其是针对银河麒麟 Kylin Linux 的不同发行版本。

确认当前系统与SSH版本信息
第一步:查看系统版本
执行以下命令获取系统详细信息:cat /etc/os-release uname -r
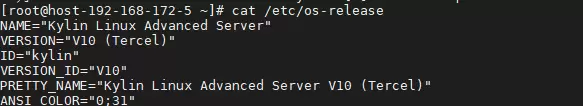 常见情况参考:
常见情况参考:- Kylin V10(桌面版) → 基于 Ubuntu 18.04/20.04
- Kylin V10(服务器版) → 基于 CentOS 7/8 或 openEuler
- Kylin V10 SP2/SP3 → 可能已预装 OpenSSH 8.7+ 或 9.x 版本
第二步:检查当前SSH版本
运行如下指令查看 OpenSSH 当前版本:ssh -V
 若输出显示为 OpenSSH 8.2p1,则系统很可能为基于 CentOS 8 的 Kylin V10 服务器版本。
若输出显示为 OpenSSH 8.2p1,则系统很可能为基于 CentOS 8 的 Kylin V10 服务器版本。
手动编译安装 OpenSSH 9.9p1(高风险操作)
警告:此方法可能导致 SSH 服务无法启动或登录失败!必须确保具备本地控制台、IPMI、VNC 或串口等备用访问方式。
提示:由于 yum 包管理器最高仅支持升级至 OpenSSH_8.2p1,因此需通过源码手动升级。
操作步骤
- 配置备用访问通道(必要前提)
如云平台 VNC 控制台、物理机键盘鼠标接入等。 - 安装编译所需依赖包
针对基于 CentOS/RHEL/Kylin 的系统:sudo yum groupinstall "Development Tools" -y sudo yum install zlib-devel openssl-devel pam-devel tcp_wrappers-devel -y - 下载并解压 OpenSSH 9.9p1 源码包
若网络受限,请在本地下载后上传至服务器。cd /opt wget https://cdn.openbsd.org/pub/OpenBSD/OpenSSH/portable/openssh-9.9p1.tar.gz tar -zxvf openssh-9.9p1.tar.gz cd openssh-9.9p1 - 配置、编译并安装
使用如下参数执行 configure,注意关键选项禁用 GSSAPI:./configure \ --prefix=/usr \ --sysconfdir=/etc/ssh \ --with-pam \ --with-ssl-engine \ --with-zlib \ --without-gssapi # 关键!禁用 GSSAPI 以消除 sha1 相关算法 make && sudo make install - 备份原始配置文件
sudo cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config /etc/ssh/sshd_config.bak - 测试新配置语法正确性
sudo /usr/sbin/sshd -t - 重启 SSH 服务
sudo systemctl restart sshd - 验证版本及算法状态
ssh -V sshd -T | grep gssapikexalgorithms # 正常情况下应无输出
方案优势
- 完全移除 GSSAPI 支持,杜绝相关弱算法暴露(如 SHA1)
- 获得最新安全补丁,包括 ssh-agent RCE 漏洞修复
--without-gssapi潜在风险
- 系统包管理器(如 yum)不再追踪该版本,后续更新需手动处理
- PAM 与 systemd 集成可能出现异常
- 若 OpenSSL 被升级,需重新编译 OpenSSH
yum/apt配置文件调整:/etc/ssh/sshd_config
[root@host-192-168-172-5 ~]# cat /etc/ssh/sshd_config
# $OpenBSD: sshd_config,v 1.103 2018/04/09 20:41:22 tj Exp $
# This is the sshd server system-wide configuration file. See
# sshd_config(5) for more information.
# This sshd was compiled with PATH=/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/sbin
# The strategy used for options in the default sshd_config shipped with
# OpenSSH is to specify options with their default value where
# possible, but leave them commented. Uncommented options override the
# default value.
# If you want to change the port on a SELinux system, you have to tell
# SELinux about this change.
# semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp #PORTNUMBER
#
Port 22222
#AddressFamily any
#ListenAddress 0.0.0.0
#ListenAddress ::
HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key
HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ecdsa_key
HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key
# Ciphers and keying
#RekeyLimit default none
# Logging
#SyslogFacility AUTH
SyslogFacility AUTH
#LogLevel INFO
# Authentication:
#LoginGraceTime 2m
PermitRootLogin yes
#StrictModes yes
#MaxAuthTries 6
#MaxSessions 10
#PubkeyAuthentication yes
# The default is to check both .ssh/authorized_keys and .ssh/authorized_keys2
# but this is overridden so installations will only check .ssh/authorized_keys
AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys
#AuthorizedPrincipalsFile none
#AuthorizedKeysCommand none
#AuthorizedKeysCommandUser nobody
# For this to work you will also need host keys in /etc/ssh/ssh_known_hosts
#HostbasedAuthentication no
# Change to yes if you don't trust ~/.ssh/known_hosts for
# HostbasedAuthentication
#IgnoreUserKnownHosts no
# Don't read the user's ~/.rhosts and ~/.shosts files
#IgnoreRhosts yes
# To disable tunneled clear text passwords, change to no here!
#PasswordAuthentication yes
PermitEmptyPasswords no
PasswordAuthentication yes
# Change to no to disable s/key passwords
#ChallengeResponseAuthentication yes
ChallengeResponseAuthentication no
# Kerberos options
#KerberosAuthentication no
#KerberosOrLocalPasswd yes
#KerberosTicketCleanup yes
#KerberosGetAFSToken no
#KerberosUseKuserok yes
# GSSAPI options
#GSSAPIAuthentication yes
#GSSAPICleanupCredentials no
#GSSAPIStrictAcceptorCheck yes
#GSSAPIKeyExchange no
#GSSAPIEnablek5users no
# Set this to 'yes' to enable PAM authentication, account processing,
# and session processing. If this is enabled, PAM authentication will
# be allowed through the ChallengeResponseAuthentication and
# PasswordAuthentication. Depending on your PAM configuration,
# PAM authentication via ChallengeResponseAuthentication may bypass
# the setting of "PermitRootLogin without-password".
# If you just want the PAM account and session checks to run without
# PAM authentication, then enable this but set PasswordAuthentication
# and ChallengeResponseAuthentication to 'no'.
# WARNING: 'UsePAM no' is not supported in kylin and may cause several
# problems.
UsePAM yes
#AllowAgentForwarding yes
#AllowTcpForwarding yes
#GatewayPorts no
X11Forwarding yes
#X11DisplayOffset 10
#X11UseLocalhost yes
#PermitTTY yes
PrintMotd no
#PrintLastLog yes
#TCPKeepAlive yes
#PermitUserEnvironment no
#Compression delayed
#ClientAliveInterval 0
#ClientAliveCountMax 3
#UseDNS no
#PidFile /var/run/sshd.pid
#MaxStartups 10:30:100
#PermitTunnel no
#ChrootDirectory none
#VersionAddendum none
# no default banner path
Banner none
AcceptEnv LANG LC_CTYPE LC_NUMERIC LC_TIME LC_COLLATE LC_MONETARY LC_MESSAGES
AcceptEnv LC_PAPER LC_NAME LC_ADDRESS LC_TELEPHONE LC_MEASUREMENT
AcceptEnv LC_IDENTIFICATION LC_ALL LANGUAGE
AcceptEnv XMODIFIERS
# override default of no subsystems
Subsystem sftp /usr/libexec/openssh/sftp-server -l INFO -f AUTH
# Example of overriding settings on a per-user basis
#Match User anoncvs
# X11Forwarding no
# AllowTcpForwarding no
# PermitTTY no
# ForceCommand cvs server
#CheckUserSplash yes
# To modify the system-wide ssh configuration, create a *.conf file under
# /etc/ssh/sshd_config.d/ which will be automatically included below
#Include /etc/ssh/sshd_config.d/*.conf
Protocol 2
LogLevel VERBOSE
PubkeyAuthentication yes
#RSAAuthentication yes
IgnoreRhosts yes
#RhostsRSAAuthentication no
HostbasedAuthentication no
PermitEmptyPasswords no
PermitUserEnvironment no
#Ciphers aes128-ctr,aes192-ctr,aes256-ctr,aes128-gcm@openssh.com,aes256-gcm@openssh.com,chacha20-poly1305@openssh.com
ClientAliveCountMax 0
Banner /etc/issue.net
#MACs hmac-sha2-512,hmac-sha2-512-etm@openssh.com,hmac-sha2-256,hmac-sha2-256-etm@openssh.com,hmac-sha1,hmac-sha1-etm@openssh.com
StrictModes yes
AllowTcpForwarding no
AllowAgentForwarding no
GatewayPorts no
PermitTunnel no
#KexAlgorithms curve25519-sha256,curve25519-sha256@libssh.org,diffie-hellman-group14-sha1,diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha1,diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha256
# 强制使用安全加密套件(覆盖默认值)
Ciphers chacha20-poly1305@openssh.com,aes256-gcm@openssh.com,aes128-gcm@openssh.com,aes256-ctr,aes192-ctr,aes128-ctr
MACs hmac-sha2-512-etm@openssh.com,hmac-sha2-256-etm@openssh.com,umac-128-etm@openssh.com
KexAlgorithms curve25519-sha256,curve25519-sha256@libssh.org,diffie-hellman-group16-sha512,diffie-hellman-group18-sha512升级后验证流程
- 确认版本号是否生效
ssh -V # 应输出:OpenSSH_9.9p1 ... - 检查 GSSAPIKexAlgorithms 是否已被清除
sshd -T | grep -i gssapi若无任何输出,则表示相关算法已成功移除。
常见问题排查
服务无法正常启动
检查错误日志中的关键信息: 错误日志关键信息:- “Missing privilege separation directory: /var/empty”
- “Failed to start daemon”
- “Address already in use”
- PAM 模块加载失败等
问题根源分析
可能原因包括:- 编译时未启用 PAM 支持但系统强制依赖
- crypto-policies 安全策略限制导致服务拒绝启动
- systemd 单元文件仍受旧规则约束
- 权限或目录缺失(如 /var/empty)
解决方案(二选一)
方案 A:【推荐】禁用 crypto-policies 对 SSH 的影响修改系统范围的加密策略,避免其干扰 SSH 启动:
sudo update-crypto-policies --set LEGACY # 或临时设为 DEFAULT 并排除冲突项重启服务后测试是否恢复。 方案 B:修改 systemd 服务文件,绕过 crypto-policies 限制
编辑服务单元文件,添加环境变量跳过策略检查:
sudo systemctl edit sshd插入以下内容:
[Service] Environment=OPENSSL_ENABLE_SHA1_SIGNATURES=1保存并重载配置:
sudo systemctl daemon-reexec sudo systemctl restart sshd
验证是否还存在 GSSAPIKexAlgorithms
执行命令:sshd -T | grep -i gssapikexalgorithms预期结果:无输出,表示该算法已被彻底移除。
最终建议操作流程
- 先确认系统版本和当前 SSH 版本
- 准备控制台或带外管理手段
- 安装开发工具链和依赖库
- 下载 OpenSSH 9.9p1 源码并编译安装
- 备份原配置,测试新配置语法
- 重启服务并验证版本和算法列表
- 如遇启动失败,优先尝试切换 crypto-policies 策略
成功后的效果
- SSH 版本显示为 OpenSSH_9.9p1- 弱加密算法(特别是涉及 GSSAPI 和 SHA1 的)不再暴露
- 扫描工具(如绿盟)不再报出“支持弱加密算法”漏洞
- 服务稳定运行,支持现有用户认证方式
gssapikexalgorithms补充说明
- 手动编译版本不会被系统自动更新覆盖,需自行维护- 建议在测试环境中先行验证全流程
- 若未来系统提供官方高版本包,可考虑回迁至包管理方式
最终总结建议
对于生产环境,优先寻求厂商提供的安全更新支持;若无可用更新,且安全合规压力较大,在可控条件下可采用手动编译方式升级至 OpenSSH 9.9p1。务必全程记录操作步骤,并保留回滚能力。检查 SSH 配置中是否仅包含 gssapiauthentication no(或其他禁用设置),且未配置 gssapikexalgorithms。
验证弱加密算法是否已清除,执行以下命令:
sshd -T | grep -E 'ciphers|macs|kexalgorithms'确保输出结果中不包含 arcfour、cbc、sha1 或 3des 等不安全算法。

服务无法正常启动。

日志分析
[root@host-192-168-172-5 ~]# sudo journalctl -u sshd -n 20 --no-pager
-- Logs begin at Sun 2025-05-18 14:11:09 CST, end at Tue 2025-11-25 15:49:04 CST. --
11月 25 15:47:23 host-192-168-172-5 sshd[3536277]: command-line: line 0: Bad configuration option: GSSAPIKexAlgorithms
11月 25 15:47:23 host-192-168-172-5 systemd[1]: sshd.service: Main process exited, code=exited, status=1/FAILURE
11月 25 15:47:23 host-192-168-172-5 systemd[1]: sshd.service: Failed with result 'exit-code'.
11月 25 15:47:23 host-192-168-172-5 systemd[1]: Failed to start OpenSSH server daemon.
11月 25 15:48:05 host-192-168-172-5 systemd[1]: sshd.service: Service RestartSec=42s expired, scheduling restart.
11月 25 15:48:05 host-192-168-172-5 systemd[1]: sshd.service: Scheduled restart job, restart counter is at 26.
11月 25 15:48:05 host-192-168-172-5 systemd[1]: Stopped OpenSSH server daemon.
11月 25 15:48:05 host-192-168-172-5 systemd[1]: Starting OpenSSH server daemon...
11月 25 15:48:06 host-192-168-172-5 sshd[3536600]: command-line: line 0: Bad configuration option: GSSAPIKexAlgorithms
11月 25 15:48:06 host-192-168-172-5 systemd[1]: sshd.service: Main process exited, code=exited, status=1/FAILURE
11月 25 15:48:06 host-192-168-172-5 systemd[1]: sshd.service: Failed with result 'exit-code'.
11月 25 15:48:06 host-192-168-172-5 systemd[1]: Failed to start OpenSSH server daemon.
11月 25 15:48:48 host-192-168-172-5 systemd[1]: sshd.service: Service RestartSec=42s expired, scheduling restart.
11月 25 15:48:48 host-192-168-172-5 systemd[1]: sshd.service: Scheduled restart job, restart counter is at 27.
11月 25 15:48:48 host-192-168-172-5 systemd[1]: Stopped OpenSSH server daemon.
11月 25 15:48:48 host-192-168-172-5 systemd[1]: Starting OpenSSH server daemon...
11月 25 15:48:48 host-192-168-172-5 sshd[3536910]: command-line: line 0: Bad configuration option: GSSAPIKexAlgorithms
11月 25 15:48:48 host-192-168-172-5 systemd[1]: sshd.service: Main process exited, code=exited, status=1/FAILURE
11月 25 15:48:48 host-192-168-172-5 systemd[1]: sshd.service: Failed with result 'exit-code'.
11月 25 15:48:48 host-192-168-172-5 systemd[1]: Failed to start OpenSSH server daemon.关键错误信息如下:
sshd[3536277]: command-line: line 0: Bad configuration option: GSSAPIKexAlgorithms在通过 systemd 启动时,系统尝试通过命令行传入特定参数:
GSSAPIKexAlgorithms然而,当前安装的 OpenSSH 版本为 9.9p1,该版本在编译过程中已禁用 GSSAPI 支持:
--without-gssapi由于二进制程序无法识别与 GSSAPI 相关的启动选项,导致解析失败并直接退出(exit 1)。
sshd问题根源
查看系统的 systemd 服务配置文件:
EnvironmentFile=-/etc/crypto-policies/back-ends/opensshserver.config
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/sshd -D $OPTIONS $CRYPTO_POLICY $PERMITROOTLOGIN其中引用的环境变量:
$CRYPTO_POLICY来源于以下配置文件:
/etc/crypto-policies/back-ends/opensshserver.config该文件内容可能包含类似如下设置:
CRYPTO_POLICY="-o GSSAPIKexAlgorithms=gss-group14-sha1-,gss-gex-sha1-"而当前使用的 OpenSSH 是手动编译且明确关闭了 GSSAPI 功能,因此:
- sshd 二进制不支持 GSSAPI 相关指令
- 启动时解析 CRYPTO_POLICY 参数失败
- 进程崩溃退出
sshd为何某些方式可以成功启动?
当你手动运行 sshd 命令时,并未加载 systemd 的环境配置:
$CRYPTO_POLICY因此不会传入导致问题的 CRYPTO_POLICY 参数,从而避免了错误。
sshd -tsshd -D -e解决方案(任选其一)
方案 A:【推荐】移除 crypto-policies 对 SSH 的影响
此方法最为彻底和安全:
- 清空或删除 crypto-policies 生成的 SSH 配置文件:
sudo rm -f /etc/crypto-policies/back-ends/opensshserver.config或创建一个空文件以防止服务报错:
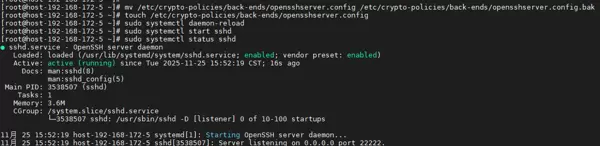
sudo touch /etc/crypto-policies/back-ends/opensshserver.config - 重新加载 systemd 配置:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload - 启动 SSH 服务:
sudo systemctl start sshd
此操作将使
$CRYPTO_POLICY为空值,不再传递任何可能导致冲突的启动参数。
-o方案 B:修改 systemd 服务文件,绕过环境变量
通过复制并编辑服务文件,强制忽略 CRYPTO_POLICY:
sudo cp /usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service /etc/systemd/system/sshd.service使用 sed 删除变量引用:
sudo sed -i 's/ \$CRYPTO_POLICY//' /etc/systemd/system/sshd.service或直接手动编辑替换以下行:
[Service]
...
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/sshd -D $OPTIONS $PERMITROOTLOGIN
...完成后执行:
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadsudo systemctl start sshdExecStart验证问题是否仍然存在
检查配置文件是否仍包含问题参数:
cat /etc/crypto-policies/back-ends/opensshserver.config若输出类似:
CRYPTO_POLICY='-o GSSAPIKexAlgorithms=...,gss-gex-sha1-'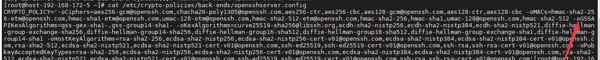
则可确认该配置正是引发故障的根本原因。
GSSAPIKexAlgorithms最终建议操作流程
- 终止所有正在运行的 sshd 进程:
sudo pkill -f "sshd" - 消除 crypto-policies 的干扰:
sudo rm -f /etc/crypto-policies/back-ends/opensshserver.configsudo touch /etc/crypto-policies/back-ends/opensshserver.config - 重载 systemd 配置:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload - 启动 SSH 服务:
sudo systemctl start sshd - 检查服务状态:
systemctl status sshd
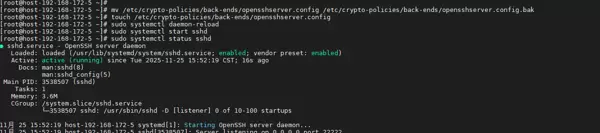
解决后的效果
systemctl status sshd→ active (running)
sshd -T | grep gssapi→ 不再出现无效参数错误
gssapikexalgorithms安全扫描工具将不再因弱算法或错误配置报告高危风险。
补充说明
OpenSSH 9.0 及以上版本默认隐藏未启用的算法,但前提是不能传入非法或无效的命令行选项。
Kylin 或 CentOS 中的 crypto-policies 机制是为系统自带的 OpenSSH 设计的,手动编译的版本需主动规避其影响。
只需执行方案 A,即可彻底解决问题。
完成之后,你的 OpenSSH 9.9p1 将以完全干净、安全且符合规范的状态稳定运行。
最终建议
针对不同环境下的服务器,推荐采取以下应对措施:
测试或非关键服务器
建议手动编译并部署 OpenSSH 9.9 及以上版本以满足安全要求。
--without-gssapi生产服务器(允许停机)
推荐将系统升级至 Kylin V10 SP3、openEuler 22.03 或 Rocky Linux 9 等支持更高 OpenSSH 版本的发行版。
生产服务器(不允许停机)
可暂维持现有配置,同时提交《误报说明》进行备案处理;
或通过部署 SSH 跳板机的方式实现安全合规与业务连续性的平衡。




 雷达卡
雷达卡




 京公网安备 11010802022788号
京公网安备 11010802022788号







