插件的基本概念
插件(Plug-in),也被称为 addin、add-on、addon 或扩展模块,是一种依照特定接口规范开发的程序组件。它无法独立运行,必须依赖于主程序所提供的运行环境,通过调用宿主系统中的函数库或数据资源来实现功能。
插件的工作机制与原理
在软件架构设计中,插件技术将整体功能划分为两个核心部分:主程序和插件模块。主程序负责提供基础框架以及标准化的接口,而插件则用于实现具体的功能逻辑。这种结构使得软件具备高度灵活性——通过增删或更新插件,即可动态调整系统的功能范围,而无需修改主程序本身。

插件的主要分类
根据实现方式和技术层次的不同,插件通常可分为以下三类:
- 文本插件:结构简单,类似于批处理脚本,适用于执行基本指令操作。
- 脚本插件:基于专用脚本语言编写,具有一定的可编程能力,常用于快速功能扩展。
- 程序插件:利用成熟开发环境构建,如C++或C#等语言编写的DLL模块,功能强大且性能优越。
插件的实际应用场景
插件技术被广泛应用于各类软件平台之中。例如,在早期IE浏览器中,用户可通过安装插件来支持特定文件格式的解析;在网站开发领域,Google Sitemaps 插件可用于生成站点地图,而类似“开心农场”的社交插件则增强了网页互动性与娱乐体验。
采用插件架构的技术优势
引入插件机制可在多个开发环节带来显著益处:
- 结构清晰:各插件相互独立,职责分明,便于理解与管理。
- 易于维护与修改:插件通过标准接口与主程序通信,支持热插拔式替换或升级。
- 高可移植性:插件由小粒度功能单元组成,复用性强,易于迁移到其他项目中。
- 灵活调整系统结构:新增或移除功能只需增减对应插件,不影响主程序稳定性。
- 低耦合度:插件之间不直接交互,仅通过主程序协调,降低模块间依赖风险。
- 开发策略灵活:可根据资源情况选择完整开发或分阶段实施,提升项目可控性。

如何创建 AFSim 插件
以下是基于 Visual Studio 开发 AFSim 兼容插件的具体步骤:
- 启动 Visual Studio 并打开开发环境。
- 选择“创建新项目”选项。
- 选用“空项目”模板进行初始化设置。
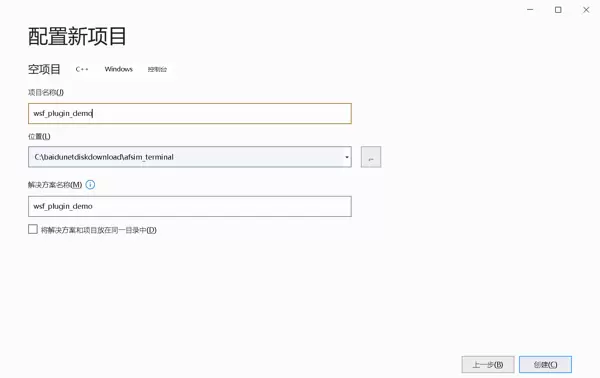
- 填写项目名称及存储路径后,点击【创建】按钮完成项目建立。
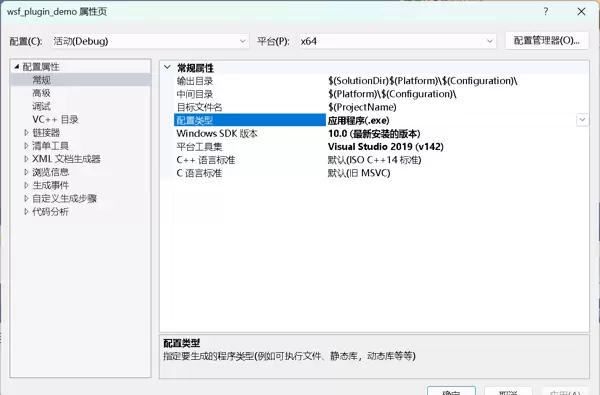
- 默认情况下,项目输出类型为可执行文件(.exe),需手动更改为动态链接库(DLL)格式以符合插件要求。
- 右键项目名称 → 属性 → 配置属性 → 常规 → 配置类型,将“应用程序(.exe)”更改为“动态库(.dll)”。



关键代码参考
可参照 AFSim 源码中的 wsf_air_combat 工程进行编码实现,主要包含以下核心文件:
- 用于与宿主程序对接的注册接口定义:【RegisterPlugin.hpp】
#ifndef RegisterPlugin_HPP
#define RegisterPlugin_HPP
#include "WsfPluginTemplate.hpp"
#include "WsfScenarioExtension.hpp"
#include "WsfSimulation.hpp"
#include "UtMemory.hpp"
class RegisterPlugin : public WsfScenarioExtension
{
public:
~RegisterPlugin() noexcept override = default;
void SimulationCreated(WsfSimulation & aSimulation) override
{
// Simulation对象创建完成后,注册Simulation扩展
// 字符串需要保持唯一性
aSimulation.RegisterExtension("wsf_plugin_demo", ut::make_unique<WsfPluginTemplate>());
}
};
#endif#include "wsfplugin_export.h"
#include "RegisterPlugin.hpp"
// wsf
#include "WsfPlugin.hpp"
#include "WsfApplication.hpp"
#include "WsfApplicationExtension.hpp"
#include "UtMemory.hpp"
extern"C"
{
WSF_PLUGIN_EXPORT void WsfPluginVersion(UtPluginVersion& aVersion)
{
aVersion = UtPluginVersion(
WSF_PLUGIN_API_MAJOR_VERSION,
WSF_PLUGIN_API_MINOR_VERSION,
WSF_PLUGIN_API_COMPILER_STRING
);
}
WSF_PLUGIN_EXPORT void WsfPluginSetup(WsfApplication& aApplication)
{
// 注册本插件工程,字符串需要保持唯一性
// 此处使用默认Application扩展
aApplication.RegisterExtension("register_wsf_plugin_demo", ut::make_unique<WsfDefaultApplicationExtension<RegisterPlugin>>());
}
}#ifndef WsfPluginTemplate_HPP
#define WsfPluginTemplate_HPP
#include "WsfSimulationExtension.hpp"
#include "UtCallbackHolder.hpp"
class WsfPlatform;
class WsfSensor;
class WsfTrack;
class WsfPluginTemplate: public WsfSimulationExtension
{
public:
WsfPluginTemplate();
~WsfPluginTemplate() noexcept override;
bool Initialize() override;
private:
void PlatformAdded(double aSimTime, WsfPlatform* aPlatformPtr);
void PlatformDeleted(double aSimTime, WsfPlatform* aPlatformPtr);
void SensorTrackUpdated(double aSimTime, WsfSensor* aSensorPtr, const WsfTrack* aTrackPtr);
void AdvanceTime(double aSimTime); // 推进时间
private:
UtCallbackHolder mCallbacks;
double mPreSimTime = 0.0;
};
#endif#include "WsfPluginTemplate.hpp"
#include "RegisterPlugin.hpp"
// WSF
#include "WsfApplication.hpp"
#include "observer/WsfPlatformObserver.hpp"
#include "observer/WsfTrackObserver.hpp"
#include "observer/WsfSimulationObserver.hpp"
#include "WsfPlatform.hpp"
#include "sensor/WsfSensor.hpp"
#include "WsfSimulation.hpp"
#include "WsfTrack.hpp"
WsfPluginTemplate::WsfPluginTemplate()
{}
WsfPluginTemplate::~WsfPluginTemplate() noexcept
{}
bool WsfPluginTemplate::Initialize()
{
mCallbacks.Add(WsfObserver::SensorTrackUpdated(&GetSimulation()).Connect(&WsfPluginTemplate::SensorTrackUpdated, this));
mCallbacks.Add(WsfObserver::SensorTrackInitiated(&GetSimulation()).Connect(&WsfPluginTemplate::SensorTrackUpdated, this));
mCallbacks.Add(WsfObserver::PlatformAdded(&GetSimulation()).Connect(&WsfPluginTemplate::PlatformAdded, this));
mCallbacks.Add(WsfObserver::PlatformDeleted(&GetSimulation()).Connect(&WsfPluginTemplate::PlatformDeleted, this));
mCallbacks.Add(WsfObserver::AdvanceTime(&GetSimulation()).Connect(&WsfPluginTemplate::AdvanceTime, this));
std::cout << "WsfPluginTemplate plugin loaded!" << std::endl;
return true;
}
void WsfPluginTemplate::PlatformAdded(double aSimTime, WsfPlatform* aPlatformPtr)
{
std::cout
<< "PlatformAdded: " << aSimTime << ", "
<< aPlatformPtr->GetName() << ", "
<< aPlatformPtr->GetType() << std::endl;
}
void WsfPluginTemplate::PlatformDeleted(double aSimTime, WsfPlatform* aPlatformPtr)
{
std::cout
<< "PlatformDeleted: " << aSimTime << ", "
<< aPlatformPtr->GetName() << ", "
<< aPlatformPtr->GetType() << std::endl;
}
void WsfPluginTemplate::SensorTrackUpdated(double aSimTime, WsfSensor* aSensorPtr, const WsfTrack* aTrackPtr)
{
double longitude, latitude, altitude;
aTrackPtr->GetLocationLLA(latitude, longitude, altitude);
std::cout
<< "SensorTrackUpdated: " << aSimTime << ", "
<< aSensorPtr->GetName() << ", "
<< aSensorPtr->GetPlatform()->GetIndex() << ", "
<< aTrackPtr->GetTargetIndex() << ", "
<< latitude << ", "
<< longitude << ", "
<< altitude << std::endl;
}
void WsfPluginTemplate::AdvanceTime(double aSimTime)
{
double deltaTime = aSimTime - mPreSimTime;
if (deltaTime < 0.0000001) return;
mPreSimTime = aSimTime;
std::cout << "AdvanceTime: " << aSimTime << std::endl;
// 获取场景所有平台,并获取平台的位置和姿态
int platformCount = GetSimulation().GetPlatformCount();
for (int i = 0; i < platformCount; ++i)
{
auto platform = GetSimulation().GetPlatformEntry(i);
std::cout << "PlatformName: " << platform->GetName() << std::endl;
std::cout << "PlatformType: " << platform->GetType() << std::endl;
// 位置(经纬高)
auto lla = platform->GetLocationLLA();
std::cout << "PlatformLocation: ";
std::cout << " Longitude: " << lla.mLon
<< " Latitude: " << lla.mLat
<< " Altitude: " << lla.mAlt << std::endl;
// 姿态(横滚 俯仰 航向)
auto ned = platform->GetOrientationNED();
std::cout << "PlatformOrientation: ";
std::cout << " Roll: " << ned.mPhi
<< " Pitch: " << ned.mTheta
<< " Heading: " << ned.mPsi << std::endl;
}
}#ifndef WSF_PLUGIN_EXPORT_H
#define WSF_PLUGIN_EXPORT_H
#ifdef WSF_PLUGIN_STATIC_DEFINE
# define WSF_PLUGIN_EXPORT
# define WSF_PLUGIN_NO_EXPORT
#else
# ifndef WSF_PLUGIN_EXPORT
# ifdef wsfplugin_EXPORTS
/* We are building this library */
# define WSF_PLUGIN_EXPORT __declspec(dllexport)
# else
/* We are using this library */
# define WSF_PLUGIN_EXPORT __declspec(dllimport)
# endif
# endif
# ifndef WSF_PLUGIN_NO_EXPORT
# define WSF_PLUGIN_NO_EXPORT
# endif
#endif
#ifndef WSF_PLUGIN_DEPRECATED
# define WSF_PLUGIN_DEPRECATED __declspec(deprecated)
#endif
#ifndef WSF_PLUGIN_DEPRECATED_EXPORT
# define WSF_PLUGIN_DEPRECATED_EXPORTWSF_PLUGIN_EXPORTWSF_PLUGIN_DEPRECATED
#endif
#ifndef WSF_PLUGIN_DEPRECATED_NO_EXPORT
# define WSF_PLUGIN_DEPRECATED_NO_EXPORTWSF_PLUGIN_NO_EXPORTWSF_PLUGIN_DEPRECATED
#endif
#if 0 /* DEFINE_NO_DEPRECATED */
# ifndef WSF_PLUGIN_NO_DEPRECATED
# define WSF_PLUGIN_NO_DEPRECATED
# endif
#endif
#endif/* WSF_PLUGIN_EXPORT_H */项目环境配置说明
为确保插件能正确编译并加载,需完成如下配置流程:
- 创建名为
afsimsdk的目录,用于存放从 AFSim 源码中提取的所有头文件和静态库文件。该目录是进行二次开发的核心依赖环境。 - 可通过提供的 Python 脚本自动提取所需头文件:

使用方法: python extract_hpp.py -s "C:\path\to\src" -d "C:\path\to\dst"
其中,src 参数指向 AFSim 项目的源码路径(如:swdev\src)。
import argparse
import os
import shutil
import json
from pathlib import Path
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Extract .hpp files preserving folder structure and print folders.")
parser.add_argument("-s", "--src", default=".", help="Source root folder to scan (default: current directory)")
parser.add_argument("-d", "--dst", default=r"c:\baidunetdiskdownload\LX\extracted_hpp", help="Destination root (default: c:\\baidunetdiskdownload\\LX\\extracted_hpp)")
args = parser.parse_args()
src_path = Path(args.src).resolve()
dst_path = Path(args.dst).resolve()
dst_path.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
# 创建一个用于存储提取后文件夹路径的缓存文件
cache_file = dst_path / "extracted_paths.json"
# 如果缓存文件存在,则加载已有的路径信息
if cache_file.exists():
with open(cache_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
cached_data = json.load(f)
seen_dirs = cached_data.get("seen_dirs", [])
copied_files = cached_data.get("copied_files", [])
else:
seen_dirs = []
copied_files = []
copied = 0
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(src_path):
root_path = Path(root)
# 输出并记录所有遍历到的文件夹路径
print(str(root_path))
if str(root_path) not in seen_dirs:
seen_dirs.append(str(root_path))
for fname in files:
if fname.lower().endswith(".hpp"):
src_file = root_path / fname
rel = src_file.relative_to(src_path).parent # 相对目录
target_dir = dst_path / rel
target_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
# 复制文件
shutil.copy2(src_file, target_dir / fname)
copied += 1
# 记录复制的文件路径
copied_file_path = str(target_dir / fname)
if copied_file_path not in copied_files:
copied_files.append(copied_file_path)
# 保存路径信息到缓存文件
cache_data = {
"seen_dirs": seen_dirs,
"copied_files": copied_files
}
with open(cache_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(cache_data, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
print(f"\n扫描完成。总共复制 .hpp 文件: {copied}")
print(f"目标位置: {dst_path}")
print(f"缓存文件位置: {cache_file}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()\bin\lib 目录下的所有 lib 文件复制到本地 sdk 库目录中。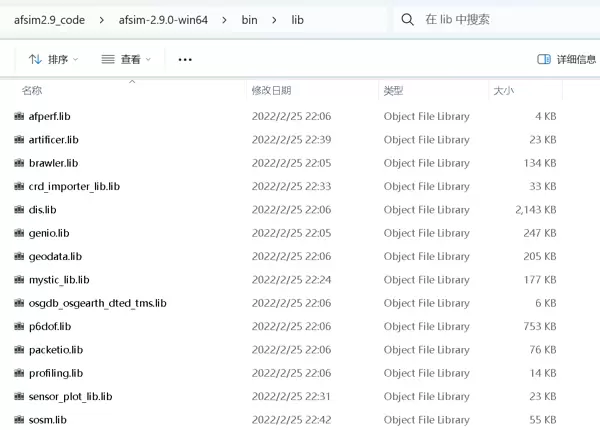
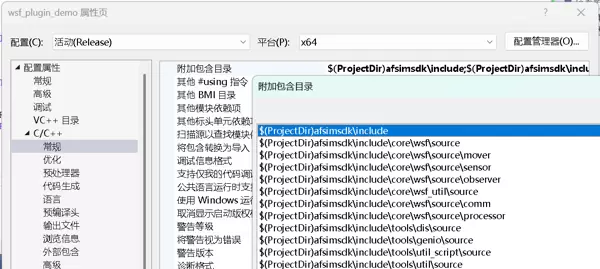
宏定义设置
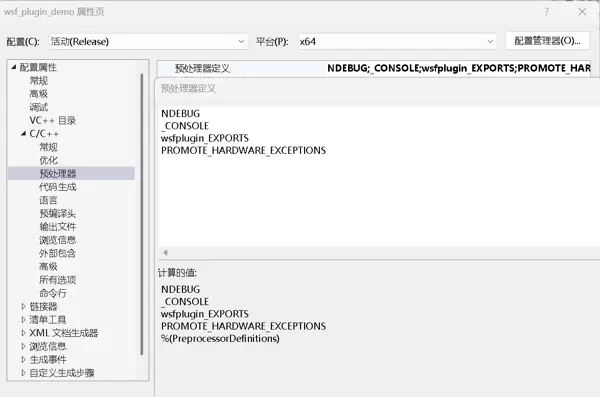
- wsfplugin_EXPORTS:此宏用于标识当前构建的是插件 DLL,在【wsfplugin_export.h】中起作用。
- PROMOTE_HARDWARE_EXCEPTIONS:对应版本标识
win_1929_64bit_release-hwe,若未定义会导致生成的插件版本信息不完整,进而无法通过宿主程序的版本校验,最终导致加载失败。
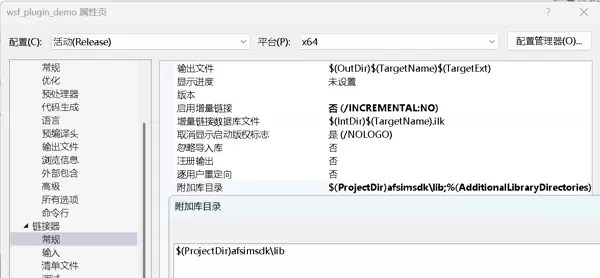
库文件引用配置
- 可以预先配置库搜索路径,也可在引用时直接指定完整路径+库名的方式避免全局配置。
- 在编译过程中可能出现链接错误,应根据错误提示逐步添加所需的库文件。
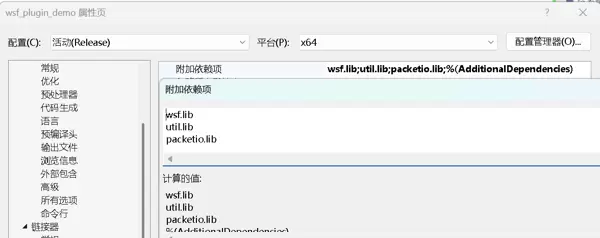
插件编译与生成
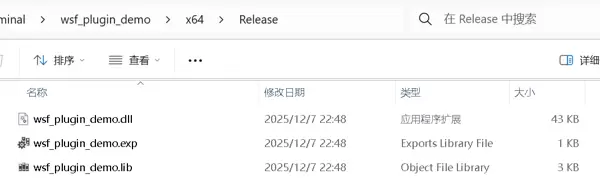
完成代码和配置后,右键项目选择“生成”,输出的 DLL 文件将按设定路径生成。
插件验证方法
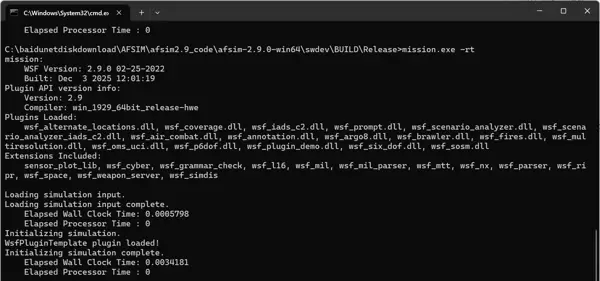
将生成的 DLL 文件复制到 AFSim 的插件目录:swdev\BUILD\Release\wsf_plugins。
随后进入 swdev\BUILD\Release 目录,使用命令行工具运行 mission.exe -rt。该命令不会加载任何场景文件,但会尝试初始化所有插件,可用于检测插件是否成功加载。
若插件正常加载,控制台将显示相应日志信息。
总结
插件技术以其良好的扩展性、模块化结构和高效的维护特性,已成为现代软件开发的重要手段之一。通过合理运用插件架构,不仅可以提升开发效率,还能增强系统的灵活性与可持续演进能力。
插件DLL已成功加载,文件输出显示在插件初始化函数【WsfPluginTemplate::Initialize()】中打印了【WsfPluginTemplate plugin loaded!】,表明插件正常运行。
初始化完成并确认加载无误后,即可基于当前插件项目开展后续功能开发与扩展工作。
相关参考资料:
AFSim_二次开发_创建AFSim开发环境




 雷达卡
雷达卡




 京公网安备 11010802022788号
京公网安备 11010802022788号







