本帖隐藏的内容
IntroductionHave you come across a situation when a Chief Marketing Officer of a company tells you – “Help me understand our customers better so that we can market our products to them in a better manner!”
I did and the analyst in me was completely clueless what to do! I was used to getting specific problems, where there is an outcome to be predicted for various set of conditions. But I had no clue, what to do in this case. If the person would have asked me to calculate Life Time Value (LTV) or propensity of Cross-sell, I wouldn’t have blinked. But this question looked very broad to me!
This is usually the first reaction when you come across a unsupervised learning problem for the first time! You are not looking for specific insights for a phenomena, but what you are looking for are structures with in data with out them being tied down to a specific outcome.
The method of identifying similar groups of data in a data set is called clustering. Entities in each group are comparatively more similar to entities of that group than those of the other groups. In this article, I will be taking you through the types of clustering, different clustering algorithms and a comparison between two of the most commonly used cluster methods.
Let’s get started.
Table of Contents
- Overview
- Types of Clustering
- Types of Clustering Algorithms
- K Means Clustering
- Hierarchical Clustering
- Difference between K Means and Hierarchical clustering
- Applications of Clustering
- Improving Supervised Learning algorithms with clustering
1. Overview
Clustering is the task of dividing the population or data points into a number of groups such that data points in the same groups are more similar to other data points in the same group than those in other groups. In simple words, the aim is to segregate groups with similar traits and assign them into clusters.
Let’s understand this with an example. Suppose, you are the head of a rental store and wish to understand preferences of your costumers to scale up your business. Is it possible for you to look at details of each costumer and devise a unique business strategy for each one of them? Definitely not. But, what you can do is to cluster all of your costumers into say 10 groups based on their purchasing habits and use a separate strategy for costumers in each of these 10 groups. And this is what we call clustering.
Now, that we understand what is clustering. Let’s take a look at the types of clustering.
2. Types of Clustering
Broadly speaking, clustering can be divided into two subgroups :
- Hard Clustering: In hard clustering, each data point either belongs to a cluster completely or not. For example, in the above example each customer is put into one group out of the 10 groups.
- Soft Clustering: In soft clustering, instead of putting each data point into a separate cluster, a probability or likelihood of that data point to be in those clusters is assigned. For example, from the above scenario each costumer is assigned a probability to be in either of 10 clusters of the retail store.
3. Types of clustering algorithms
Since the task of clustering is subjective, the means that can be used for achieving this goal are plenty. Every methodology follows a different set of rules for defining the ‘similarity’ among data points. In fact, there are more than 100 clustering algorithms known. But few of the algorithms are used popularly, let’s look at them in detail:
- Connectivity models: As the name suggests, these models are based on the notion that the data points closer in data space exhibit more similarity to each other than the data points lying farther away. These models can follow two approaches. In the first approach, they start with classifying all data points into separate clusters & then aggregating them as the distance decreases. In the second approach, all data points are classified as a single cluster and then partitioned as the distance increases. Also, the choice of distance function is subjective. These models are very easy to interpret but lacks scalability for handling big datasets. Examples of these models are hierarchical clustering algorithm and its variants.
- Centroid models: These are iterative clustering algorithms in which the notion of similarity is derived by the closeness of a data point to the centroid of the clusters. K-Means clustering algorithm is a popular algorithm that falls into this category. In these models, the no. of clusters required at the end have to be mentioned beforehand, which makes it important to have prior knowledge of the dataset. These models run iteratively to find the local optima.
- Distribution models: These clustering models are based on the notion of how probable is it that all data points in the cluster belong to the same distribution (For example: Normal, Gaussian). These models often suffer from overfitting. A popular example of these models is Expectation-maximization algorithm which uses multivariate normal distributions.
- Density Models:These models search the data space for areas of varied density of data points in the data space. It isolates various different density regions and assign the data points within these regions in the same cluster. Popular examples of density models are DBSCAN and OPTICS.
Now I will be taking you through two of the most popular clustering algorithms in detail – K Means clustering and Hierarchical clustering. Let’s begin.
4. K Means Clustering
K means is an iterative clustering algorithm that aims to find local maxima in each iteration. This algorithm works in these 5 steps :
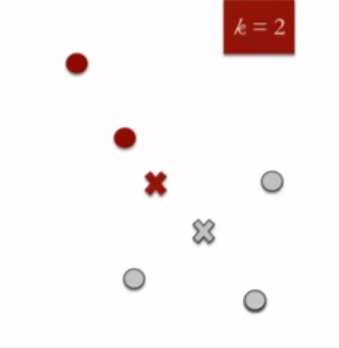
- Specify the desired number of clusters K : Let us choose k=2 for these 5 data points in 2-D space.
- Randomly assign each data point to a cluster : Let’s assign three points in cluster 1 shown using red color and two points in cluster 2 shown using grey color.
- Compute cluster centroids : The centroid of data points in the red cluster is shown using red cross and those in grey cluster using grey cross.
- Re-assign each point to the closest cluster centroid : Note that only the data point at the bottom is assigned to the red cluster even though its closer to the centroid of grey cluster. Thus, we assign that data point into grey cluster
- Re-compute cluster centroids : Now, re-computing the centroids for both the clusters.
- Repeat steps 4 and 5 until no improvements are possible : Similarly, we’ll repeat the 4th and 5th steps until we’ll reach global optima. When there will be no further switching of data points between two clusters for two successive repeats. It will mark the termination of the algorithm if not explicitly mentioned.
5. Hierarchical Clustering
Hierarchical clustering, as the name suggests is an algorithm that builds hierarchy of clusters. This algorithm starts with all the data points assigned to a cluster of their own. Then two nearest clusters are merged into the same cluster. In the end, this algorithm terminates when there is only a single cluster left.
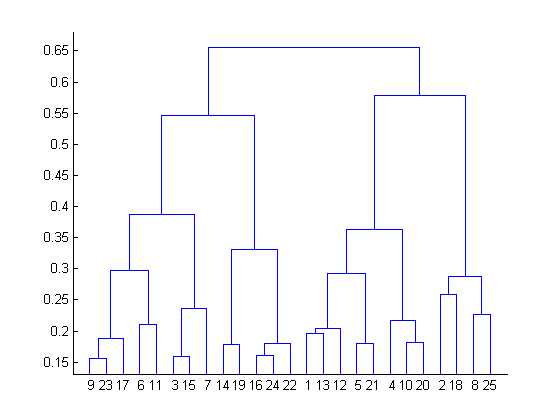
The results of hierarchical clustering can be shown using dendrogram. The dendrogram can be interpreted as:
At the bottom, we start with 25 data points, each assigned to separate clusters. Two closest clusters are then merged till we have just one cluster at the top. The height in the dendrogram at which two clusters are merged represents the distance between two clusters in the data space.
The decision of the no. of clusters that can best depict different groups can be chosen by observing the dendrogram. The best choice of the no. of clusters is the no. of vertical lines in the dendrogram cut by a horizontal line that can transverse the maximum distance vertically without intersecting a cluster.
In the above example, the best choice of no. of clusters will be 4 as the red horizontal line in the dendrogram below covers maximum vertical distance AB.
Two important things that you should know about hierarchical clustering are:
- This algorithm has been implemented above using bottom up approach. It is also possible to follow top-down approach starting with all data points assigned in the same cluster and recursively performing splits till each data point is assigned a separate cluster.
- The decision of merging two clusters is taken on the basis of closeness of these clusters. There are multiple metrics for deciding the closeness of two clusters :
- Euclidean distance: ||a-b||2 = √(Σ(ai-bi))
- Squared Euclidean distance: ||a-b||22 = Σ((ai-bi)2)
- Manhattan distance: ||a-b||1 = Σ|ai-bi|
- Maximum distance:||a-b||INFINITY = maxi|ai-bi|
- Mahalanobis distance: √((a-b)T S-1 (-b)) {where, s : covariance matrix}




 雷达卡
雷达卡
























 京公网安备 11010802022788号
京公网安备 11010802022788号







