本帖隐藏的内容
IntroductionWith growing need of data science managers, we need tools which take out difficulty from doing data science and make it fun. Not everyone is willing to learn coding, even though they would want to learn / apply data science. This is where GUI based tools can come in handy.
Today, I will introduce you to another GUI based tool – Orange. This tool is great for beginners who wish to visualize patterns and understand their data without really knowing how to code.
In my previous article, I presented you with another GUI based tool KNIME. If you do not want to learn to code but still apply data science, you can try out any of these tools.
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll be able to predict which person out of a certain set of people is eligible for a loan with Orange!
Table of Contents:
- Why Orange?
- Setting up your System:
- Creating your first Workflow
- Familiarizing yourself with the basics
- Problem Statement
- Importing the data files
- Understanding the data
- How do you clean your data?
- Training your first model
1. Why Orange?
Orange is a platform built for mining and analysis on a GUI based workflow. This signifies that you do not have to know how to code to be able to work using Orange and mine data, crunch numbers and derive insights.
You can perform tasks ranging from basic visuals to data manipulations, transformations, and data mining. It consolidates all the functions of the entire process into a single workflow.
The best part and the differentiator about Orange is that it has some wonderful visuals. You can try silhouettes, heat-maps, geo-maps and all sorts of visualizations available.
2. Setting up your SystemOrange comes built-in with the Anaconda tool if you’ve previously installed it. If not, follow these steps to download Orange.
Step 1: Go to https://orange.biolab.si and click on Download.

Step 2: Install the platform and set the working directory for Orange to store its files.

This is what the start-up page of Orange looks like. You have options that allow you to create new projects, open recent ones or view examples and get started.
Before we delve into how Orange works, let’s define a few key terms to help us in our understanding:
- A widget is the basic processing point of any data manipulation. It can do a number of actions based on what you choose in your widget selector on the left of the screen.
- A workflow is the sequence of steps or actions that you take in your platform to accomplish a particular task.
You can also go to “Example Workflows” on your start-up screen to check out more workflows once you have created your first one.
For now, click on “New” and let’s start building your first workflow.
3. Creating Your First Workflow
This is the first step towards building a solution to any problem. We need to first understand what steps we need to take in order to achieve our final goal. After you clicked on “New” in the above step, this is what you should have come up with.

This is your blank Workflow on Orange. Now, you’re ready to explore and solve any problem by dragging any widget from the widget menu to your workflow.
4. Familiarising yourself with the basics
Orange is a platform that can help us solve most problems in Data Science today. Topics that range from the most basic visualizations to training models. You can even evaluate and perform unsupervised learning on datasets:
4.1 Problem
The problem we’re looking to solve in this tutorial is the practice problem Loan Prediction that can be accessed via this link on Datahack.
4.2 Importing the data files
We begin with the first and the necessary step to understand our data and make predictions: importing our data

Step 1: Click on the “Data” tab on the widget selector menu and drag the widget “File” to our blank workflow.
Step 2: Double click the “File” widget and select the file you want to load into the workflow. In this article, as we will be learning how to solve the practice problem Loan Prediction, I will import the training dataset from the same.

Step 3: Once you can see the structure of your dataset using the widget, go back by closing this menu.
Step 4: Now since we have the raw .csv details, we need to convert it to a format we can use in our mining. Click on the dotted line encircling the “File” widget and drag, and then click anywhere in the blank space.

Step 5: As we need a data table to better visualize our findings, we click on the “Data Table” widget.
Step 6: Now double click the widget to visualize your table.

Neat! Isn’t it?
Let’s now visualize some columns to find interesting patterns in our data.
4.3 Understanding our Data
4.3.1 Scatter Plot
Click on the semicircle in front of the “File” widget and drag it to an empty space in the workflow and select the “Scatter Plot” widget.

Once you create a Scatter Plot widget, double click it and explore your data like this! You can select the X and Y axes, colors, shapes, sizes and a lot of other manipulations.

The plot I’ve explored is a Gender by Income plot, with the colors set to the education levels. As we can see in males, the higher income group naturally belongs to the Graduates!
Although in females, we see that a lot of the graduate females are earning low or almost nothing at all. Any specific reason? Let’s find out using the scatterplot.

One possible reason I found was marriage. A huge number graduates who were married were found to be in lower income groups; this may be due to family responsibilities or added efforts. Makes perfect sense, right?
4.3.2 Distribution
Another way to visualize our distributions would be the “Distributions” widget. Click on the semi-circle again, and drag to find the widget “Distributions”.

Now double click on it and visualize!

What we see is a very interesting distribution. We have in our dataset, more number of married males than females.




 雷达卡
雷达卡





















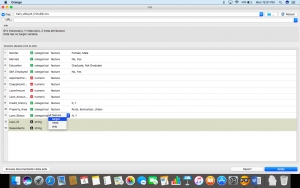

 Step 7: Now, click on the “Test and Score” widget to see how well your model is doing.
Step 7: Now, click on the “Test and Score” widget to see how well your model is doing.









 京公网安备 11010802022788号
京公网安备 11010802022788号







