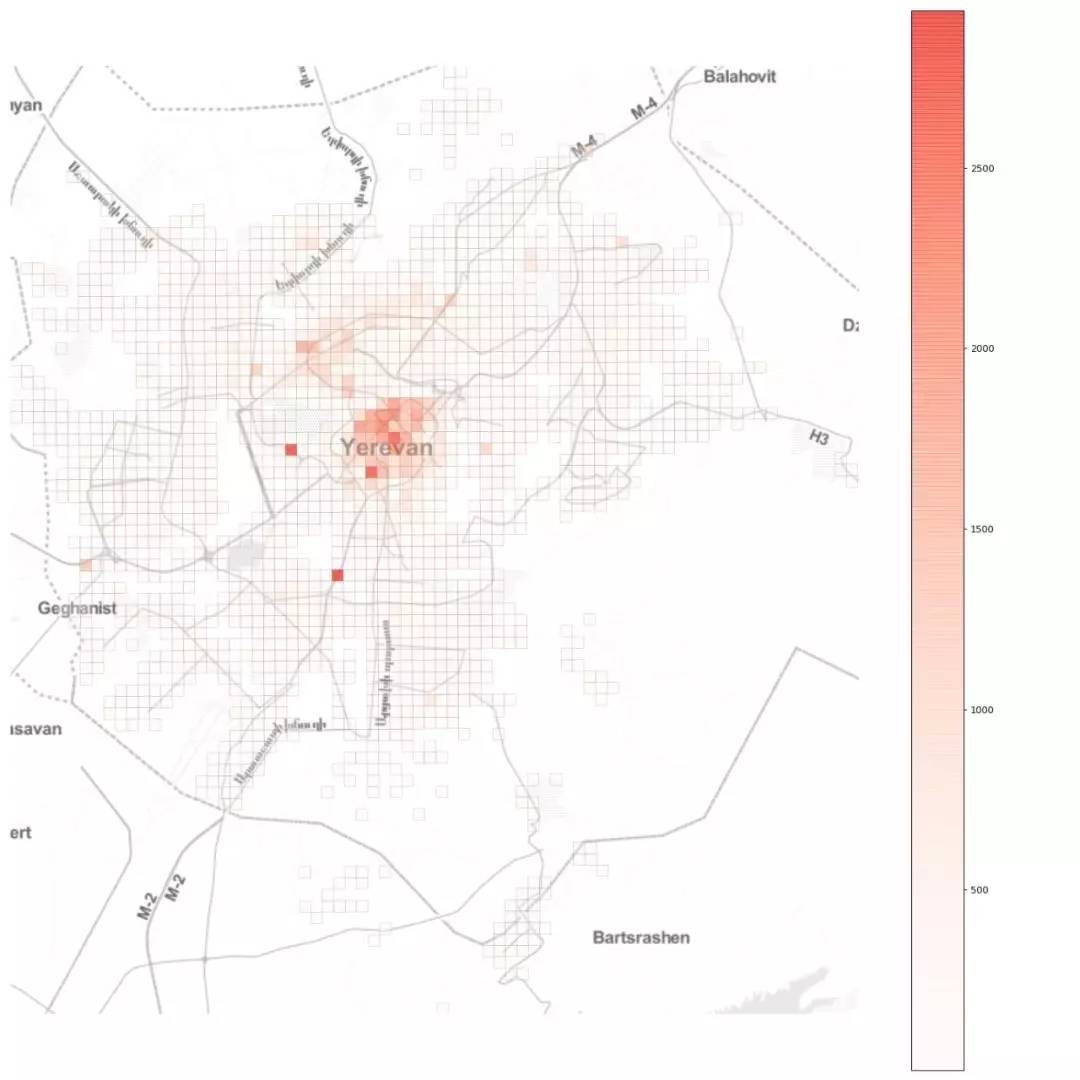
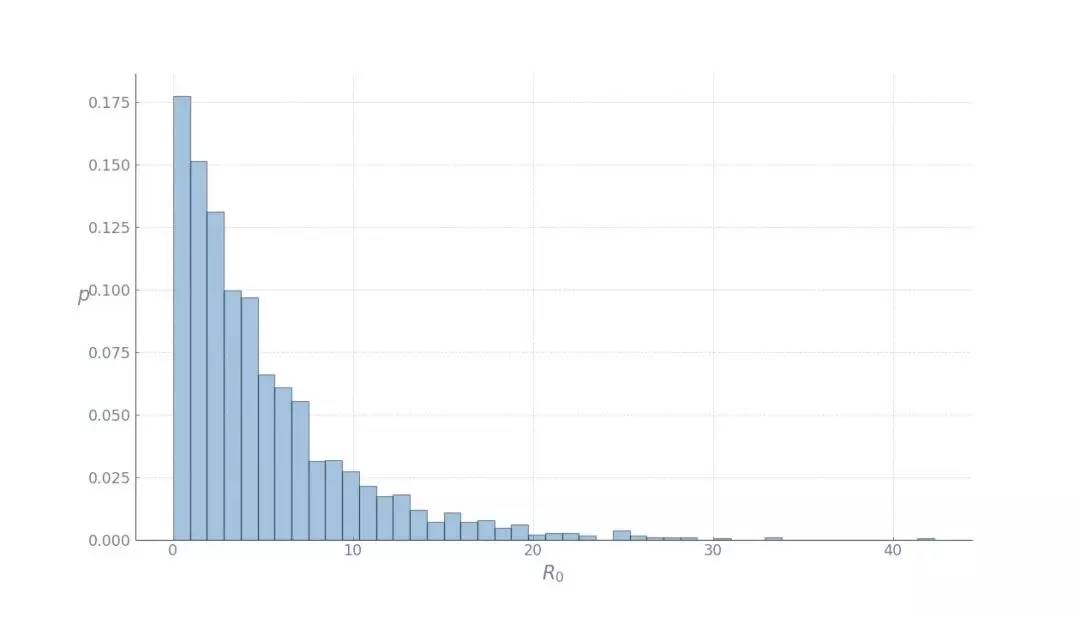
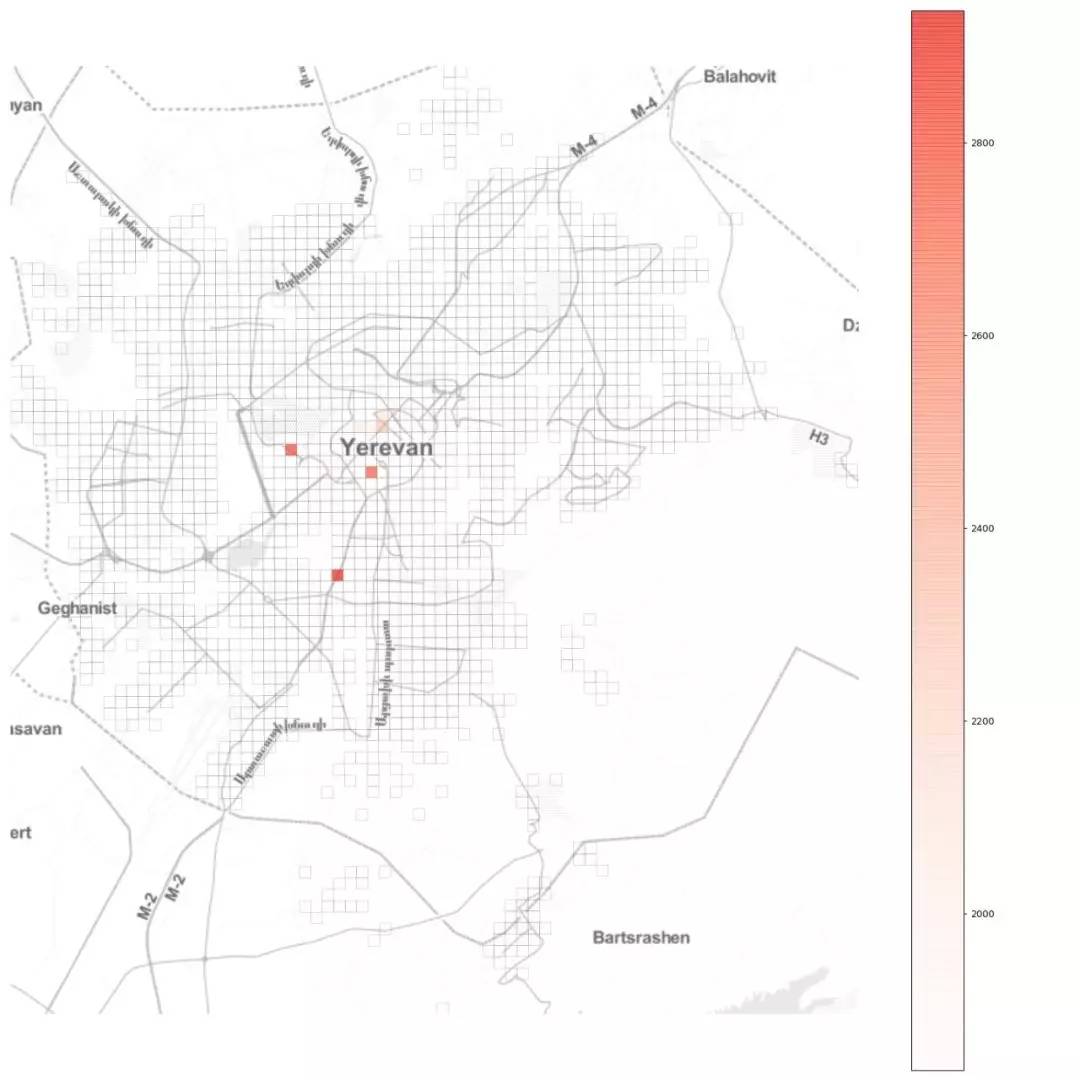
目前,尚未发现经医疗研究标准确认的特效药。此外,很多重要的流行病学指标仍属未知,如基本传染数 R0(在流行病学上,基本传染数指在没有外力介入,同时所有人都没有免疫力的情况下,一个感染到某种传染病的人,会把疾病传染给其他多少个人的平均数)。新型冠状病毒还存在很多的不确定性。 如今的全球社会,联通度和流动性空前。由于小世界效应,这类流行病对全球造成重大威胁。有人猜想如果 2020 年发生全球性灾难事件(粗略定义为伤亡人数大于 1 亿),那么最可能的原因是某种流行病,而不是核灾难、气候灾难等。全球城市化的快速发展更加强化了这一点,因为人口密集的城市变成了疾病扩散网络中的传播节点,因而变得极度脆弱。 本文将探讨当一座城市遭受流行病袭击时会发生什么,应立即采取哪些措施,以及这些措施对城市规划、政策制定和管理带来的影响。本文以亚美尼亚共和国首都埃里温作为案例,对冠状病毒在该城市中的蔓延情况进行数学建模和模拟,并观察城市流动模式对病毒传播的影响。 城市流动 高效持续的城市流动对现代城市的运转举足轻重,并直接影响城市的宜居性和和经济输出(GDP)。但是,当流行病爆发时,城市流动却火上浇油,推动了疾病的传播。 我们先来看埃里温市起讫点(origin-destination,OD)交通流以聚集的方式在均匀笛卡尔网格上形成的网络,以便了解城市流动模式的空间结构:自去年12月以来,新型冠状病毒所引发的疫情已经给城市活动带来了很大影响。怎样确切了解病毒的传播过程,从而帮助城市更好提出措施?使用建模的方法也能起到一些作用。本文是一篇Python教程,教你在家中也可以建模疫情传播。本文以亚美尼亚共和国首都埃里温作为案例,对冠状病毒在该城市中的蔓延情况进行数学建模和模拟,并观察城市流动模式对病毒传播的影响。读者也可根据文末的示例代码,自己上手使用。


S_i,t:尚未感染或易感人群(易感组);
I_i,t:感染该疾病且具备传染性的人口(感染组);
R_i,t:感染疾病后,由于痊愈或死亡从感染组移出的人口。这组人不再感染病毒,也不会将病毒传播给他人。
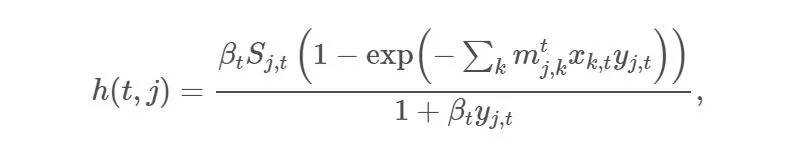
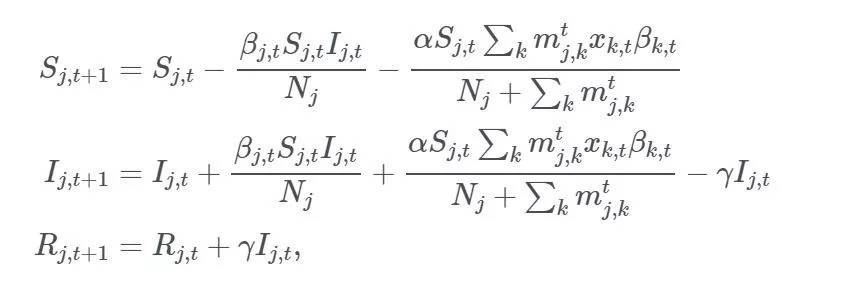
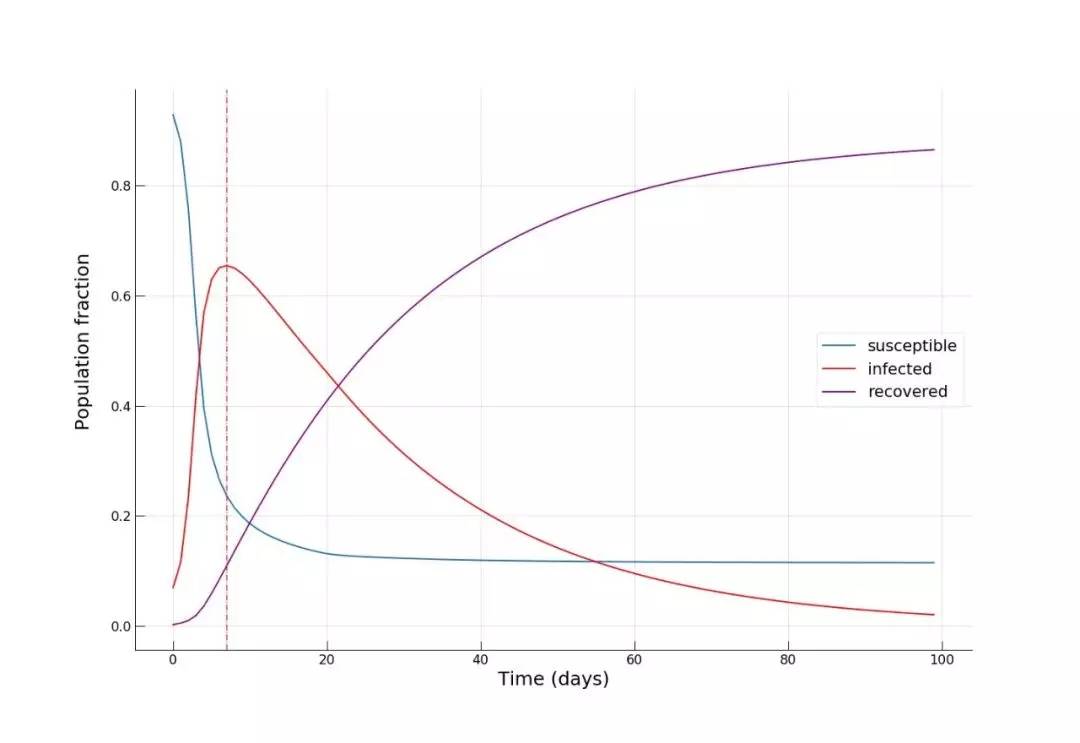



- import numpy as np
- # initialize the population vector from the origin-destination flow matrix
- N_k = np.abs(np.diagonal(OD) + OD.sum(axis=0) - OD.sum(axis=1))
- locs_len = len(N_k) # number of locations
- SIR = np.zeros(shape=(locs_len, 3)) # make a numpy array with 3 columns for keeping track of the S, I, R groups
- SIR[:,0] = N_k # initialize the S group with the respective populations
- first_infections = np.where(SIR[:, 0]<=thresh, SIR[:, 0]//20, 0) # for demo purposes, randomly introduce infections
- SIR[:, 0] = SIR[:, 0] - first_infections
- SIR[:, 1] = SIR[:, 1] + first_infections # move infections to the I group
- # row normalize the SIR matrix for keeping track of group proportions
- row_sums = SIR.sum(axis=1)
- SIR_n = SIR / row_sums[:, np.newaxis]
- # initialize parameters
- beta = 1.6
- gamma = 0.04
- public_trans = 0.5 # alpha
- R0 = beta/gamma
- beta_vec = np.random.gamma(1.6, 2, locs_len)
- gamma_vec = np.full(locs_len, gamma)
- public_trans_vec = np.full(locs_len, public_trans)
- # make copy of the SIR matrices
- SIR_sim = SIR.copy()
- SIR_nsim = SIR_n.copy()
- # run model
- print(SIR_sim.sum(axis=0).sum() == N_k.sum())
- from tqdm import tqdm_notebook
- infected_pop_norm = []
- susceptible_pop_norm = []
- recovered_pop_norm = []
- for time_step in tqdm_notebook(range(100)):
- infected_mat = np.array([SIR_nsim[:,1],]*locs_len).transpose()
- OD_infected = np.round(OD*infected_mat)
- inflow_infected = OD_infected.sum(axis=0)
- inflow_infected = np.round(inflow_infected*public_trans_vec)
- print('total infected inflow: ', inflow_infected.sum())
- new_infect = beta_vec*SIR_sim[:, 0]*inflow_infected/(N_k + OD.sum(axis=0))
- new_recovered = gamma_vec*SIR_sim[:, 1]
- new_infect = np.where(new_infect>SIR_sim[:, 0], SIR_sim[:, 0], new_infect)
- SIR_sim[:, 0] = SIR_sim[:, 0] - new_infect
- SIR_sim[:, 1] = SIR_sim[:, 1] + new_infect - new_recovered
- SIR_sim[:, 2] = SIR_sim[:, 2] + new_recovered
- SIR_sim = np.where(SIR_sim<0,0,SIR_sim)
- # recompute the normalized SIR matrix
- row_sums = SIR_sim.sum(axis=1)
- SIR_nsim = SIR_sim / row_sums[:, np.newaxis]
- S = SIR_sim[:,0].sum()/N_k.sum()
- I = SIR_sim[:,1].sum()/N_k.sum()
- R = SIR_sim[:,2].sum()/N_k.sum()
- print(S, I, R, (S+I+R)*N_k.sum(), N_k.sum())
- print('\n')
- infected_pop_norm.append(I)
- susceptible_pop_norm.append(S)
- recovered_pop_norm.append(R)
原文地址:http://edu.cda.cn/article/163




 雷达卡
雷达卡











 京公网安备 11010802022788号
京公网安备 11010802022788号







