一、决策树是什么?—— 通俗易懂的核心概念?
决策树(Decision Tree)是机器学习中监督学习算法的重要代表,因其逻辑类似于人类的决策过程而得名。想象你判断 “是否出门野餐”:首先看 “是否有雨”,再考虑 “温度是否适宜”,最后查看 “有无同伴”—— 这种逐步判断的逻辑链,就是决策树的核心思想。
在机器学习中,决策树的结构包含三个关键部分:
- 根节点:决策的起点(如 “是否有雨”),对应数据集中的特征
- 内部节点:中间判断条件(如 “温度是否适宜”)
- 叶节点:最终决策结果(如 “出门野餐” 或 “不出门”)
分支:每个判断的可能结果(是 / 否、数值区间等)
决策树的优势在于可解释性极强(能清晰看到决策过程)、无需特征标准化、对异常值不敏感,缺点是容易过拟合(后续会讲优化方法)。
二、决策树如何 “做决策”?—— 核心算法原理?
决策树的关键在于如何选择最优特征作为节点,本质是通过 “纯度提升” 实现分类 / 回归。常用的特征选择指标有 3 种:
- 信息增益(ID3 算法)
- 基于 “信息熵”(衡量数据混乱程度),信息增益 = 父节点熵 - 子节点加权熵。信息增益越大,说明该特征分类效果越好。
- 信息熵公式(二分类问题):
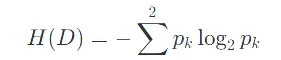
是类别 k 在数据集 D 中的占比。
- 信息增益比(C4.5 算法)
- 解决 ID3 算法偏好取值多的特征(如 “用户 ID”)的问题,引入 “特征固有值” 进行标准化:
- 信息增益比 = 信息增益 / 特征固有值
- 基尼系数(CART 算法)
- 衡量数据集的不纯度,基尼系数越小,数据纯度越高:
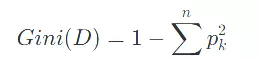
CART 树是二叉树(每个节点仅分两个分支),可同时用于分类和回归(回归时用平方误差最小化)。
三、决策树的优缺点分析
优点:
- 无需数据预处理:对数据标准化要求较低
- 处理混合数据类型:能同时处理数值型和类别型特征
- 非参数方法:不对数据分布做假设
缺点:
- 过拟合风险:随着层数增加,容易过度拟合训练数据
- 不稳定性:数据微小变化可能导致完全不同的树结构
- 偏向于多值属性:信息增益倾向于选择有更多取值的属性
四、决策树的构建与终止条件
构建过程:
- 选择最佳划分属性
- 根据属性值划分数据集
- 对每个子集递归执行上述过程
终止条件:
- 当前节点所有样本属于同一类别
- 没有剩余属性可用于进一步划分
- 当前节点样本集为空
- 达到预设的树深度或节点最小样本数
五、属性划分方法
- 信息增益(ID3 算法)
- 选择使信息增益最大的属性进行划分
- 信息增益 = 父节点熵 - 加权子节点熵之和
- 倾向于选择多值属性,可能导致过拟合
- 增益率(C4.5 算法)
- 对信息增益进行规范化,克服多值属性偏好
- 增益率 = 信息增益 / 分裂信息
- 基尼指数(CART 算法)
- 衡量数据不纯度,选择使基尼指数下降最快的属性
- 基尼指数越小,数据纯度越高
六、剪枝策略:防止过拟合
1. 预剪枝(Pre-pruning)
原理:在树构建过程中提前停止生长
方法:
- 设置最大深度
- 设置节点最小样本数
- 通过验证集评估是否继续划分
优点:
- 降低过拟合风险
- 减少训练和测试时间
缺点:
- 可能欠拟合
- 难以确定最优停止条件
2. 后剪枝(Post-pruning)
原理:先构建完整树,再自底向上剪枝
方法:
- 用验证集评估子树替换为叶节点的影响
- 若精度不下降则剪枝
优点:
- 保留更多分支可能,欠拟合风险低
- 泛化能力通常优于预剪枝
缺点:
- 计算成本较高
- 过拟合风险仍存在
七、决策树学习的目标
决策树学习的核心目标是获得泛化能力强的模型,即在未见数据上表现良好的决策树。为实现这一目标,需要:
- 选择合适的划分准则
- 设置合理的停止条件
- 应用适当的剪枝策略
- 可能使用集成方法(如随机森林)进一步提升性能
八、实战演练
这是一个关于是否可以成功申请信贷的表格,接下来同学们,请根据表格内容编写代码
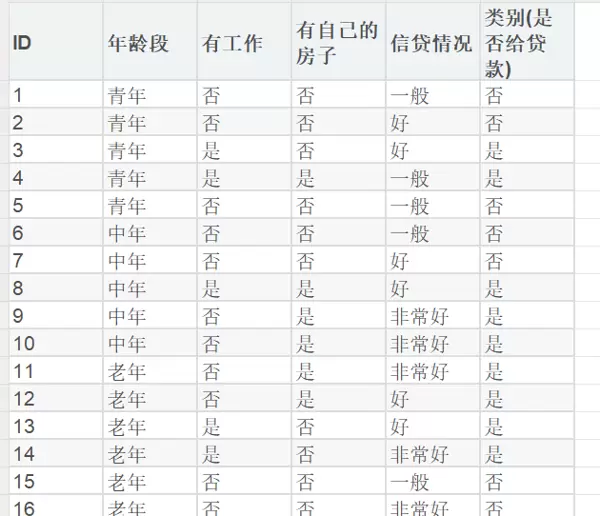
- 构建树:
- 计算熵
- 寻找最佳划分
- 信息增益
- C4.5 增益率
- 结果
def _build_tree(self, X, y, depth=0):
n_samples, n_features = X.shape
n_classes = len(np.unique(y))
# 终止条件
if (self.max_depth is not None and depth >= self.max_depth) or \
n_classes == 1 or \
n_samples < self.min_samples_split:
leaf_value = self._compute_leaf_value(y)
return TreeNode(value=leaf_value)
best_feature, best_threshold = self._find_best_split(X, y, n_features)
if best_feature is None:
return TreeNode(value=self._compute_leaf_value(y))
left_idxs = X[:, best_feature] <= best_threshold
right_idxs = ~left_idxs
left = self._build_tree(X[left_idxs], y[left_idxs], depth + 1)
right = self._build_tree(X[right_idxs], y[right_idxs], depth + 1)
return TreeNode(feature_idx=best_feature, threshold=best_threshold, left=left, right=right)def _entropy(self, y):
counts = np.bincount(y)
ps = counts / len(y)
return -np.sum([p * np.log2(p) for p in ps if p > 0])def _find_best_split(self, X, y, n_features):
best_gain = -1
best_feature = None
best_threshold = None
for feature_idx in range(n_features):
thresholds = np.unique(X[:, feature_idx])
for threshold in thresholds:
gain = self._information_gain(X, y, feature_idx, threshold)
if gain > best_gain:
best_gain = gain
best_feature = feature_idx
best_threshold = threshold
return best_feature, best_threshold公式:Gain(D,A)=H(D) - Σ(∣Dv∣/∣D∣ * H(Dv))
def _information_gain(self, X, y, feature_idx, threshold):
parent_entropy = self._entropy(y)
left_idxs = X[:, feature_idx] <= threshold
right_idxs = ~left_idxs
if np.sum(left_idxs) == 0 or np.sum(right_idxs) == 0:
return 0
n = len(y)
n_left, n_right = np.sum(left_idxs), np.sum(right_idxs)
e_left = self._entropy(y[left_idxs])
e_right = self._entropy(y[right_idxs])
child_entropy = (n_left / n) * e_left + (n_right / n) * e_right
information_gain = parent_entropy - child_entropy
return information_gain公式:增益率 = 信息增益 / 划分信息
def _split_info(self, X, feature_idx, threshold):
left_idxs = X[:, feature_idx] <= threshold
right_idxs = ~left_idxs
n = len(X)
n_left, n_right = np.sum(left_idxs), np.sum(right_idxs)
if n_left == 0 or n_right == 0:
return 0
p_left = n_left / n
p_right = n_right / n
return -p_left * np.log2(p_left) - p_right * np.log2(p_right)
def _information_gain_ratio(self, X, y, feature_idx, threshold):
information_gain = self._information_gain(X, y, feature_idx, threshold)
split_information = self._split_info(X, feature_idx, threshold)
if split_information == 0:
return 0
return information_gain / split_informationimport numpy as np
from collections import Counter
def load_data(file_path):
data = []
with open(file_path, 'r') as f:
for line in f:
items = line.strip().split(',')
items = [int(item) for item in items]
data.append(items)
return np.array(data)
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, feature_idx=None, threshold=None, value=None, left=None, right=None):
self.feature_idx = feature_idx
self.threshold = threshold
self.value = value
self.left = left
self.right = right
def is_leaf(self):
return self.value is not None
class DecisionTree:
def __init__(self, max_depth=None, min_samples_split=2):
self.max_depth = max_depth
self.min_samples_split = min_samples_split
self.root = None
def fit(self, X, y):
self.root = self._build_tree(X, y)
def predict(self, X):
return np.array([self._traverse_tree(x, self.root) for x in X])
def _traverse_tree(self, x, node):
if node.is_leaf():
return node.value
if x[node.feature_idx] <= node.threshold:
return self._traverse_tree(x, node.left)
else:
return self._traverse_tree(x, node.right)
def _build_tree(self, X, y, depth=0):
n_samples, n_features = X.shape
n_classes = len(np.unique(y))
# 终止条件
if (self.max_depth is not None and depth >= self.max_depth) or \
n_classes == 1 or \
n_samples < self.min_samples_split:
leaf_value = self._compute_leaf_value(y)
return TreeNode(value=leaf_value)
best_feature, best_threshold = self._find_best_split(X, y, n_features)
if best_feature is None:
return TreeNode(value=self._compute_leaf_value(y))
left_idxs = X[:, best_feature] <= best_threshold
right_idxs = ~left_idxs
left = self._build_tree(X[left_idxs], y[left_idxs], depth + 1)
right = self._build_tree(X[right_idxs], y[right_idxs], depth + 1)
return TreeNode(feature_idx=best_feature, threshold=best_threshold, left=left, right=right)
def _find_best_split(self, X, y, n_features):
pass
def _compute_leaf_value(self, y):
pass
class ID3DecisionTree(DecisionTree):
def __init__(self, max_depth=None, min_samples_split=2):
super().__init__(max_depth, min_samples_split)
def _entropy(self, y):
counts = np.bincount(y)
ps = counts / len(y)
return -np.sum([p * np.log2(p) for p in ps if p > 0])
def _information_gain(self, X, y, feature_idx, threshold):
parent_entropy = self._entropy(y)
left_idxs = X[:, feature_idx] <= threshold
right_idxs = ~left_idxs
if np.sum(left_idxs) == 0 or np.sum(right_idxs) == 0:
return 0
n = len(y)
n_left, n_right = np.sum(left_idxs), np.sum(right_idxs)
e_left = self._entropy(y[left_idxs])
e_right = self._entropy(y[right_idxs])
child_entropy = (n_left / n) * e_left + (n_right / n) * e_right
information_gain = parent_entropy - child_entropy
return information_gain
def _find_best_split(self, X, y, n_features):
best_gain = -1
best_feature = None
best_threshold = None
for feature_idx in range(n_features):
thresholds = np.unique(X[:, feature_idx])
for threshold in thresholds:
gain = self._information_gain(X, y, feature_idx, threshold)
if gain > best_gain:
best_gain = gain
best_feature = feature_idx
best_threshold = threshold
return best_feature, best_threshold
def _compute_leaf_value(self, y):
return Counter(y).most_common(1)[0][0]
class C45DecisionTree(DecisionTree):
def __init__(self, max_depth=None, min_samples_split=2):
super().__init__(max_depth, min_samples_split)
def _entropy(self, y):
counts = np.bincount(y)
ps = counts / len(y)
return -np.sum([p * np.log2(p) for p in ps if p > 0])
def _split_info(self, X, feature_idx, threshold):
left_idxs = X[:, feature_idx] <= threshold
right_idxs = ~left_idxs
n = len(X)
n_left, n_right = np.sum(left_idxs), np.sum(right_idxs)
if n_left == 0 or n_right == 0:
return 0
p_left = n_left / n
p_right = n_right / n
return -p_left * np.log2(p_left) - p_right * np.log2(p_right)
def _information_gain_ratio(self, X, y, feature_idx, threshold):
parent_entropy = self._entropy(y)
left_idxs = X[:, feature_idx] <= threshold
right_idxs = ~left_idxs
if np.sum(left_idxs) == 0 or np.sum(right_idxs) == 0:
return 0
n = len(y)
n_left, n_right = np.sum(left_idxs), np.sum(right_idxs)
e_left = self._entropy(y[left_idxs])
e_right = self._entropy(y[right_idxs])
child_entropy = (n_left / n) * e_left + (n_right / n) * e_right
information_gain = parent_entropy - child_entropy
split_information = self._split_info(X, feature_idx, threshold)
if split_information == 0:
return 0
gain_ratio = information_gain / split_information
return gain_ratio
def _find_best_split(self, X, y, n_features):
best_gain_ratio = -1
best_feature = None
best_threshold = None
for feature_idx in range(n_features):
thresholds = np.unique(X[:, feature_idx])
for threshold in thresholds:
gain_ratio = self._information_gain_ratio(X, y, feature_idx, threshold)
if gain_ratio > best_gain_ratio:
best_gain_ratio = gain_ratio
best_feature = feature_idx
best_threshold = threshold
return best_feature, best_threshold
def _compute_leaf_value(self, y):
return Counter(y).most_common(1)[0][0]
def evaluate_model(model, X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test):
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
test_pred = model.predict(X_test)
test_acc = np.sum(test_pred == y_test) / len(y_test)
print(f"测试集准确率: {test_acc:.4f}")
return test_acc
def main():
train_path = "C:/Users/Administrator/Downloads/dataset.txt"
test_path = "C:/Users/Administrator/Downloads/testset.txt"
train_data = load_data(train_path)
test_data = load_data(test_path)
# 分割特征和标签
X_train = train_data[:, :-1]
y_train = train_data[:, -1]
X_test = test_data[:, :-1]
y_test = test_data[:, -1]
print("\n使用ID3决策树(信息增益):")
id3_tree = ID3DecisionTree(max_depth=5)
id3_test_acc = evaluate_model(id3_tree, X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test)
print("\n使用C4.5决策树(信息增益率):")
c45_tree = C45DecisionTree(max_depth=5)
c45_test_acc = evaluate_model(c45_tree, X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()



 雷达卡
雷达卡




 京公网安备 11010802022788号
京公网安备 11010802022788号







