来源b站UP主ChrisKim_ZHT的解析
一、向量vector---#include<vector>
1.1 常见操作
- 创建
vector<int> vet;//长度为0,无内容。 vector<int> vet1(100,1);//第一个为长度,第二个为每个元素初值。 vector<vector<int>> dp(5/*行数*/,vector<int>(6,1)/*列数(长度,初值)*/);//二维数组 vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp2(5,vector<vector<int>> (6,vector<int> (4,1))) ;//三维数组 - 追加
vector<int> arr; arr.push_back(1); arr.push_back(2); for(auto &ele:arr) cout<<ele<<endl; - 移除末尾
//尾删 arr.pop_back(); for(auto &ele:arr) cout<<ele<<endl; - 获取尺寸
cout<<arr.size()<<endl; - 清除全部
?arr.clear(); - 检查是否为空
cout<<arr.empty()<<endl;//yes,return ture(1);no,return false(0). - 调整尺寸
?arr.resize(5,3);//第一个为修改长度,第二个是初值
1.2 应用场合
如果使用int mat[100010][100010];会浪费内存,可能导致MLE。
推荐使用vector<vector<int>> mat(m+10,vector<int> (n+10))
1.3 注意事项
预先设定尺寸
小心size_t溢出。.size();返回值类型为size_t,溢出将变为0。
二、栈stack---#include<stack>
2.1 创建
//构造
stack<double> stk;
stk.push(1.0);//进栈
stk.push(1.4);
cout<<stk.top()<<endl;
stk.pop();//出栈
cout<<stk.top()<<endl;
cout<<stk.size()<<endl;//取大小
cout<<stk.empty()<<endl;//判断是否为空
//也可以把vector当成栈使用
vector<int> vct;
vct.push_back(1.0);
vct.push_back(1.4);
cout<<vct.back()<<endl;2.2 适用场景
无需考虑性能瓶颈,直接使用。vector也可作为栈使用
2.3 注意
不可访问内部元素
以下为错误示例
for(auto ele:stk)
cout<<stk<<endl;三、队列queue
3.1 常见操作
queue<int> que;
//进队
que.push(1);
que.push(2);
que.push(3);
cout<<que.front()<<endl;//队首
cout<<que.back()<<endl;//队尾
//出队
que.pop()
//返回大小
que.size()
//是否为空
que.empty();3.2 使用场景
无需考虑性能瓶颈
3.3 注意
与栈相同
四、优先队列priority_queue
4.1 常见操作
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> p_que//小顶堆
priority_queue<int> pque//大顶堆
p_que.push(1);
p_que.push(2);
p_que.push(3);
cout<<p_que.top()<<endl;//取最大值
p_que.pop();4.2 适用场景
每次向队列插入不确定大小的元素或取出最大/最小元素,元素数量n,插入次数k
每次插入快速排序k * nlog n
优先队列维护k*log n
4.3 注意
仅顶部堆可读
所有元素不可修改
如需修改则可以
int x=p_que.top();
p_que.pop();
p_que.push(x+1);五、集合
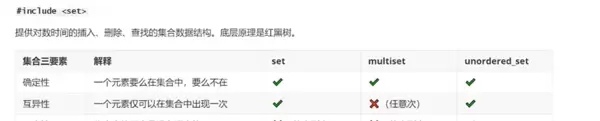
5.1 常见操作
set<int> se;
se.insert(1);//插入,且存在互异性
se.insert(1);
se.insert(2);
se.erase(2);//擦除
se.find()//查找
if(se.find(1)!=se.end())
cout<<"yes";
se.count(1)//查找存在几个
cout<<se.size();
se.clear();
cout<<se.empty();
//遍历
for(set<int>::iterator it = st.begin();it != st.end();++it)
cout<<*it<<endl;
for(auto &ele:st)
cout<<ele<<endl;5.2 适用场景
元素去重{1,1,2,2,3,4}-->{1,2,3,4}
维持顺序{1,5,3,7,9}-->{1,3,5,7,9}
检查元素是否存在
bool vis[100]
vis[1]=ture;
当数组里的数为1e19,无法编译。
用set
set<int> st;
st.insert(1);
st.insert(2);
if(count(1))
cout<<"yes"<<endl;5.3 注意
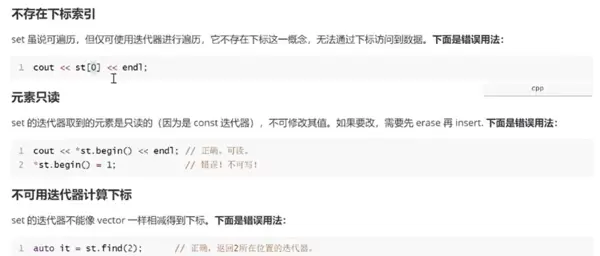
六、映射map---#include<map>

6.1 创建
map<int,int> mp;//从整型到整型的映射
mp[2]=1;
mp[2]=2;
cout<<mp[2];
if(mp.find(2)!=mp.end())
cout<<"yes"<<endl;
mp.erase();
cout<<mp.count(1);//出现次数
cout<<mp.size();
mp.clear;
cout<<mp.empty();
//遍历
mp[2]=1;
mp[1]=3;
mp[0]=5;
for(map<int,int>::iterator it=mp.begin();it!=mp.end();i++)
cout<<it->first<<" "<<it->second<<endl;
for(auto &pr:mp)
cout<<pr.first<<pr.second;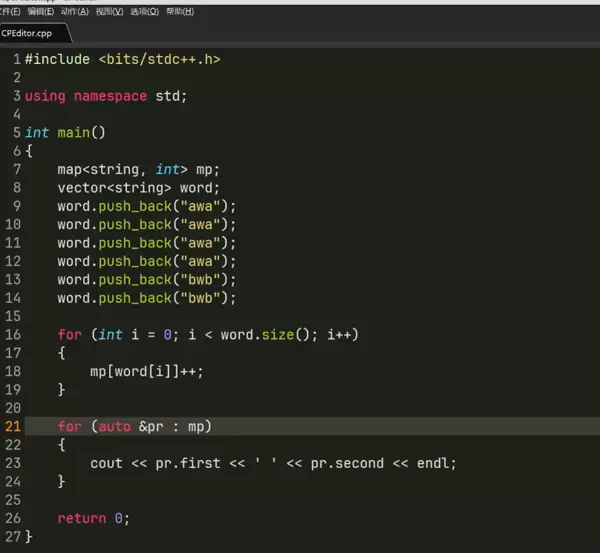
七、字符串String
7.1 常见操作
- 创建
构造函数:
string(长度, 初值)string s1; // 构造字符串,为空 string s2 = "awa!"; // 构造字符串,并赋值awa! string s3(10, '6'); // 构造字符串,通过构造函数构造为6666666666 - 输入输出
C++
string s; cin >> s; cout << s;C
string s; char buf[100]; scanf("%s", &buf); s = buf; printf("%s", s.c_str()); - 其他
功能
[]s[1] = 'a';用途
==if (s1 == s2) ...字符串拼接
+string s = s1 + s2;追加字符串
+=s += "awa";提取子串
.substr(起始下标, 子串长度)string sub = s.substr(2, 10);搜索字符串
.find(字符串, 起始下标)int pos = s.find("awa");数值与字符串互转(C++11)
源 目标 函数 int / long long / float / double / long double string to_string() string int stoi() string long long stoll() string float stof() string double stod() string long double stold()
7.2 应用场景
非常实用!建议放弃字符数组,尽快采用string。
7.3 注意事项
追加字符串务必使用
+=通常字符串长度可能非常长,使用 + 操作字符串容易导致TLE。
// 优化前: 15139ms
string s;
for (int i = 0; i < 5e5; i++)
s = s + "a";
// 优化后: < 1ms (计时器显示0)
string s;
for (int i = 0; i < 5e5; i++)
s += "a";.substr()方法的特殊参数 必须注意,C++ string 的提取子串的第一个参数是 子串起始索引 ,第二个参数是 子串长度 。 第二个参数不是子串结束点!不是子串结束点!需与 Java 等其他语言区分。
.find()方法的复杂性 该方法实现为暴力匹配,时间复杂度为O(n2)。
八、二元组pair
#include <utility>8.1 常见操作
- 创建
pair<第一个值类型, 第二个值类型> pr第一种类型:要存储的第一个值的数据类型
第二种类型:要存储的第二个值的数据类型
pair<int, int> p1; pair<int, long long> p2; pair<char, int> p3; // ... - 赋值
传统方式
pair<int, char> pr = make_pair(1, 'a');列表初始化 C++11
pair<int, char> pr = {1, 'a'}; - 取值
直接取值
获取第一个值:
.first获取第二个值:
.secondpair<int, char> pr = {1, 'a'}; int awa = pr.first; char bwb = pr.second;结构化绑定 C++17
pair<int, char> pr = {1, 'a'}; auto &[awa, bwb] = pr; - 比较
直接使用
==运算符
pair<int, int> p1 = {1, 2}; pair<int, int> p2 = {1, 3}; if (p1 == p2) { ... } // false
8.2 适用场景
任何需要二元组的情况都可使用,效率与自定义结构体相当。
8.3 注意事项
无
九、迭代器简介
3.1 迭代器是什么?
不谈抽象概念,直接看例子。
对于一个vector,我们可以使用下标遍历:
for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++)
cout << a[i] << endl;同时也可以使用迭代器遍历:
for (vector<int>::iterator it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); ++it)
cout << *it << endl;a.begin()是一个迭代器,指向首个元素
a.end()是一个迭代器,指向最后一个元素之后的位置
上述迭代器具备自增运算符,自增时迭代器将移至下一个元素。
迭代器类似于指针,若对其使用解引用运算符,即
*it3.2 为何需要迭代器?
许多数据结构并非线性(比如红黑树),针对这类非线性数据结构,索引没有实际意义。无法利用索引来遍历整个数据结构。
迭代器的功能在于定义特定数据结构的遍历方法,通过迭代器的增加或减少,表示当前遍历的位置,从而能够有效遍历非线性结构。
比如,set 的底层实现基于红黑树,我们无法借助索引来访问元素。然而,借助迭代器,我们可以遍历 set 中的元素:
for (set<int>::iterator it = st.begin(); it != st.end(); ++it)
cout << *it << endl;3.3 迭代器应用
以 vector 容器为例,其迭代器功能较为全面:
.begin():起始迭代器
.end():结束迭代器
.rbegin():逆向起始迭代器
.rend():逆向结束迭代器
迭代器
+整型:将迭代器向后推进
迭代器
-整型:将迭代器向前推进
迭代器
++:将迭代器向后推进一位
迭代器
--:将迭代器向前推进一位
迭代器
-迭代器:两个迭代器间的距离
迭代器
prev(it):返回 it 的前一个迭代器
next(it):返回 it 的后一个迭代器
对于其他容器,由于其结构特点,上述功能可能并不完全适用(例如 set 的迭代器不支持求距离的操作)
3.4 常见疑问
.end()和
.rend()指向的位置是没有实际意义的值
对于长度为 10 的数组:
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++),第 10 位是无法访问的
对于长度为 10 的容器:
for (auto it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); ++it),.end 是无法访问的
不同容器的迭代器功能可能存在差异
迭代器具体分为正向、逆向和双向,每个容器支持的运算符也可能各不相同,因此不同容器的迭代器细节可能会有所不同。
执行删除操作时需谨慎
为何 3 没被删除?
vector<int> a{1, 2, 3, 4};
for (auto it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); ++it)
if (*it == 2 || *it == 3)
a.erase(it);
// a = [1, 3, 4]为何出现 RE 错误?
vector<int> a{1, 2, 3, 4};
for (auto it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); ++it)
if (*it == 4)
a.erase(it);建议:除非必要,否则避免使用迭代器操作容器。(遍历与访问无关)
4 常用算法
4.1 总览
标记了勾选的将在本次详细讨论,其他则是在算法竞赛中推荐学习的,未在列表中出现的基本在比赛中较少使用。
(许多函数功能简单,自己也能迅速编写,但使用这些函数可以提高代码的可读性,这一点在比赛中至关重要)
算法库 Algorithm
[ ]count()find()fill()swap()
[x]reverse()
[ ]shuffle()C++11
[x]unique()
[x]sort()
[x]lower_bound()
/upper_bound()
[x]max()
/min()
[ ]max_element()min_element()prev_permutation()next_permutation()数学函数 cmath
[x]abs()
[x]exp()
[x]log()
/log10()log2()pow()
[x]sqrt()
[ ]sin()cos()tan()asin()acos()atan()sinh()cosh()tanh()asinh()acosh()atanh()C++11
[x]ceil()
/floor()
[x]round()
C++11
数值算法 numeric
[ ]iota()C++11
[ ]accumulate()gcd()
C++17
[x]lcm()
C++17
伪随机数生成 random
[ ]mt19937random_device()4.2
swap()交换两个变量的值
使用示例
template< class T >
void swap( T& a, T& b );int a = 0, b = 1;
swap(a, b);
// now a = 1, b = 0
int arr[10] {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
swap(arr[4], arr[6]);
// now arr = {0, 1, 2, 3, 6, 5, 4, 7, 8, 9}注意事项
此 swap 参数采用引用形式,无需像 C 语言那样传递地址。
4.3
sort()使用快速排序对一个可迭代对象进行排序
使用示例
template< class RandomIt, class Compare >
void sort( RandomIt first, RandomIt last, Compare comp );默认按升序排序
vector<int> arr{1, 9, 1, 9, 8, 1, 0};
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end());
// arr = [0, 1, 1, 1, 8, 9, 9]若需按降序排列,则需传入比较器。
vector<int> arr{1, 9, 1, 9, 8, 1, 0};
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end(), greater<int>());
// arr = [9, 9, 8, 1, 1, 1, 0]若需完成特殊排序,则需自定义比较器。
比较器函数返回值为布尔类型,参数为需要比较的两个元素。假设我们定义的比较操作为??:
若?a?b,则比较器函数应返回
true若?a??b,则比较器函数应返回
false注意:
若?a=b,比较器函数必须返回
falsebool cmp(pair<int, int> a, pair<int, int> b) {
if (a.second != b.second)
return a.second < b.second;
return a.first > b.first;
}
int main() {
vector<pair<int, int>> arr{{1, 9}, {2, 9}, {8, 1}, {0, 0}};
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end(), cmp);
}// arr = [(0, 0), (8, 1), (2, 9), (1, 9)]
}
4.4
lower_bound()/
upper_bound()在已升序排列的元素中,利用二分搜索查找特定元素,返回匹配元素的迭代器位置。
如果未找到,则返回尾部迭代器。
lower_bound(): 查找?≥x?的首个元素的位置
upper_bound(): 查找?>x?的首个元素的位置
如何寻找?≤x?/?<x?的首个元素呢?
?>x?的首个元素的前一元素(如果存在)即为?≤x?的首个元素
?≥x?的首个元素的前一元素(如果存在)即为?<x?的首个元素
返回的是迭代器,要转换成下标索引怎么办?减去起始迭代器即可。
用法示例
template< class ForwardIt, class T >
ForwardIt lower_bound( ForwardIt first, ForwardIt last, const T& value );vector<int> arr{0, 1, 1, 1, 8, 9, 9};
vector<int>::iterator it = lower_bound(arr.begin(), arr.end(), 7);
int idx = it - arr.begin();
// idx = 4我们常写成一行:
vector<int> arr{0, 1, 1, 1, 8, 9, 9};
idx = lower_bound(arr.begin(), arr.end(), 7) - arr.begin(); // 4
idx = lower_bound(arr.begin(), arr.end(), 8) - arr.begin(); // 4
idx = upper_bound(arr.begin(), arr.end(), 7) - arr.begin(); // 4
idx = upper_bound(arr.begin(), arr.end(), 8) - arr.begin(); // 54.5
reverse()反转一个可迭代对象的元素顺序
用法示例
template< class BidirIt >
void reverse( BidirIt first, BidirIt last );vector<int> arr(10);
iota(arr.begin(), arr.end(), 1);
// 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
reverse(arr.begin(), arr.end());
// 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 14.6
max()/
min()返回最大值 / 最小值的数值
用法示例
int mx = max(1, 2); // 2
int mn = min(1, 2); // 1自 C++11 之后,可以使用列表初始化语法传递一个列表,这样就能同时为多个元素求最大值而不必嵌套:
// Before C++11
int mx = max(max(1, 2), max(3, 4)); // 4
int mn = min(min(1, 2), min(3, 4)); // 1
// After C++11
int mx = max({1, 2, 3, 4}); // 4
int mn = min({1, 2, 3, 4}); // 14.7
unique()移除数组中相邻的重复元素,数组长度保持不变,但有效数据缩短,返回有效数据结尾的迭代器。
例如:[1,1,4,5,1,4]→[1,4,5,1,4,?―],下划线处为返回的迭代器指向。
template< class ForwardIt >
ForwardIt unique( ForwardIt first, ForwardIt last );用法示例
单独使用 unique 无法实现去重效果,因为它仅移除相邻的重复元素。但如果序列已排序,那么它可以去重。
然而,去重后,序列末尾将出现一些无效数据:[1,1,2,4,4,4,5]→[1,2,4,5,?―,?,?],为了删除这些无效数据,需结合 erase.
最终,为 vector 去重的写法为:
vector<int> arr{1, 2, 1, 4, 5, 4, 4};
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end());
arr.erase(unique(arr.begin(), arr.end()), arr.end());4.8 数学函数
所有函数参数均支持
int/
long long/
float/
double/
long double公式
示例
f(x)=|x|
abs(-1.0)f(x)=e^x
exp(2)f(x)=ln x
log(3)f(x,y)=x^y
pow(2, 3)f(x)=sqrt(x)
sqrt(2)f(x)=floor(x)
ceil(2.1)f(x)=ceil(x)
floor(2.1)f(x)=round(x)
round(2.1)注意事项
由于浮点误差,某些数学函数的行为可能不符合预期,导致错误答案。如果你的操作数均为整型,那么采用以下写法更为稳妥。
原始地址:
https://codeforces.com/blog/entry/107717
?a/b?
避免使用:
floor(1.0 * a / b)推荐使用:
a / b?a/b?
避免使用:
ceil(1.0 * a / b)推荐使用:
(a + b - 1) / b(?a/b?=(a+b-1)/b?)
?a?
避免使用:
(int) sqrt(a)推荐使用:二分查找
https://io.zouht.com/7.html
a/b
避免使用:
pow(a, b)推荐使用:快速幂
https://io.zouht.com/18.html
?log2(a)?
避免使用:
log2(a)推荐使用:
__lg(不规范,但在竞赛中适用)/
bit_width(C++20 可用)
4.9
gcd()/
lcm()(C++17)返回最大公约数 / 最小公倍数
int x = gcd(8, 12); // 4
int y = lcm(8, 12); // 24如果不是 C++17,但使用 GNU 编译器(g++),则可以使用内建函数
__gcd()当然,
gcd/
lcm函数也容易编写,直接编写即可(欧几里得算法):
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (!b)
return a;
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
int lcm(int a, int b)
{
return a / gcd(a, b) * b;
}



 雷达卡
雷达卡




 京公网安备 11010802022788号
京公网安备 11010802022788号







