第九章方差分析
9.2 ANOVA 模型拟合
9.2.1 aov()函数
aov(formula, data = NULL, projections =FALSE, qr = TRUE,
contrasts = NULL, ...)


9.2.2 表达式中各项的顺序
y ~ A + B + A:B
有三种类型的方法可以分解等式右边各效应对y所解释的方差。R默认类型I
类型I(序贯型)
效应根据表达式中先出现的效应做调整。A不做调整,B根据A调整,A:B交互项根据A和
B调整。
类型II(分层型)
效应根据同水平或低水平的效应做调整。A根据B调整,B依据A调整,A:B交互项同时根
据A和B调整。
类型III(边界型)
每个效应根据模型其他各效应做相应调整。A根据B和A:B做调整,A:B交互项根据A和B
调整。
9.3 单因素方差分析
> library(multcomp)
> attach(cholesterol)
> table(trt) #各组样本大小
trt
1time 2times4times drugD drugE
10 10 10 10 10
> aggregate(response,by=list(trt),FUN=mean)#各组均值
Group.1 x
1 1time 5.78197
2 2times 9.22497
3 4times 12.37478
4 drugD 15.36117
5 drugE 20.94752
> aggregate(response,by=list(trt),FUN=sd) #各组标准差
Group.1 x
1 1time 2.878113
2 2times 3.483054
3 4times 2.923119
4 drugD 3.454636
5 drugE 3.345003
> fit<-aov(response~trt)
> summary(fit) #检验组间差异(ANOVA)
Df SumSq Mean Sq F value Pr(>F)
trt 41351.4 337.8 32.43 9.82e-13 ***
Residuals 45 468.8 10.4
---
Signif. codes:
0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
> library(gplots)
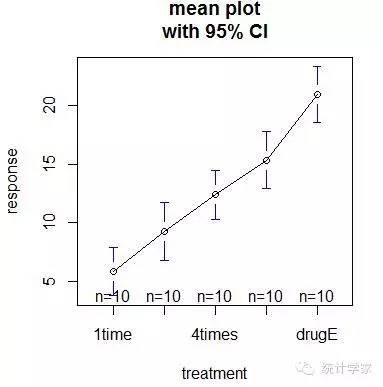
> plotmeans(response~trt,xlab="treatment",ylab="response",main="meanplot\nwith 95% CI")
#绘制各组均值及其置信区间的图形
> detach(cholesterol)
9.3.1 多重比较
TukeyHSD()函数提供了对各组均值差异的成对检验。但要注意TukeyHSD()函数与HH包存在兼容性问题:若载入HH包,TukeyHSD()函数将会失效。使用detach("package::HH")将它从搜寻路径中删除,然后再调用TukeyHSD()
> detach("package:HH", unload=TRUE)
> TukeyHSD(fit)
Tukey multiplecomparisons of means
95% family-wise confidence level
Fit: aov(formula = response ~ trt)
$trt
diff lwr upr p adj
2times-1time 3.44300 -0.6582817 7.5442820.1380949
4times-1time 6.59281 2.4915283 10.6940920.0003542
drugD-1time 9.57920 5.4779183 13.680482 0.0000003
drugE-1time 15.16555 11.0642683 19.266832 0.0000000
4times-2times 3.14981 -0.9514717 7.2510920.2050382
drugD-2times 6.13620 2.0349183 10.2374820.0009611
drugE-2times 11.72255 7.6212683 15.8238320.0000000
drugD-4times 2.98639 -1.1148917 7.0876720.2512446
drugE-4times 8.57274 4.4714583 12.6740220.0000037
drugE-drugD 5.58635 1.4850683 9.687632 0.0030633
> par(las=2)
> par(mar=c(5,8,4,2))
> plot(TukeyHSD(fit))

multcomp包中的glht()函数提供了多重均值比较更为全面的方法,既适用于线性模型,也适用于广义线性模型.
> library(multcomp)
> par(mar=c(5,4,6,2))
> tuk<-glht(fit,linfct=mcp(trt="Tukey"))
> plot(cld(tuk,level=.5),col="lightgrey")

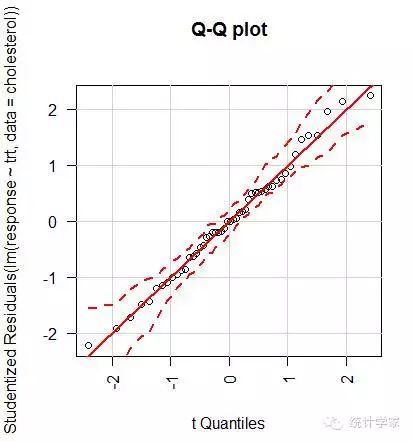
9.3.2 评估检验的假设条件
> library(car)
> qqPlot(lm(response~trt,data=cholesterol),simulate=TRUE,main="Q-Qplot",labels=FALSE)
Bartlett检验:
> bartlett.test(response~trt,data=cholesterol)
Bartlett test ofhomogeneity of variances
data: response by trt
Bartlett's K-squared = 0.5797, df = 4,
p-value = 0.9653
方差齐性分析对离群点非常敏感。可利用car包中的outlierTest()函数来检测离群点:
> library(car)
> outlierTest(fit)
No Studentized residuals withBonferonni p < 0.05
Largest |rstudent|:
rstudent unadjusted p-value Bonferonni p
19 2.251149 0.029422 NA
9.4 单因素协方差分析
单因素协方差分析(ANCOVA)扩展了单因素方差分析(ANOVA),包含一个或多个定量的
协变量
> data(litter,package="multcomp")
> attach(litter)
> table(dose)
dose
0 5 50 500
20 19 18 17
> aggregate(weight,by=list(dose),FUN=mean)
Group.1 x
1 0 32.30850
2 5 29.30842
3 50 29.86611
4 500 29.64647
> fit<-aov(weight~gesttime+dose)
> summary(fit)
Df Sum Sq Mean Sq Fvalue Pr(>F)
gesttime 1 134.3 134.30 8.049 0.00597 **
dose 3 137.1 45.71 2.739 0.04988 *
Residuals 69 1151.3 16.69
---
Signif. codes:
0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’0.1 ‘ ’ 1
由于使用了协变量,要获取调整的组均值——即去除协变量效应后的组均值。可使
用effects包中的effects()函数来计算调整的均值:
> library(effects)
> effect("dose",fit)
dose effect
dose
0 5 50 500
32.35367 28.87672 30.56614 29.33460
对用户定义的对照的多重比较
> library(multcomp)
> contrast<-rbind("no drugvs. drug"=c(3,-1,-1,-1))
> summary(glht(fit,linfct=mcp(dose=contrast)))
Simultaneous Tests for General LinearHypotheses
Multiple Comparisons of Means: User-definedContrasts
Fit: aov(formula = weight ~ gesttime +dose)
Linear Hypotheses:
Estimate Std. Error tvalue
no drug vs. drug == 0 8.284 3.209 2.581
Pr(>|t|)
no drug vs. drug == 0 0.012 *
---
Signif. codes:
0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’0.1 ‘ ’ 1
(Adjusted p values reported --single-step method)
9.4.1 评估检验的假设条件
检验回归斜率的同质性
> library(multcomp)
> fit2<-aov(weight~gesttime*dose,data=litter)
> summary(fit2)
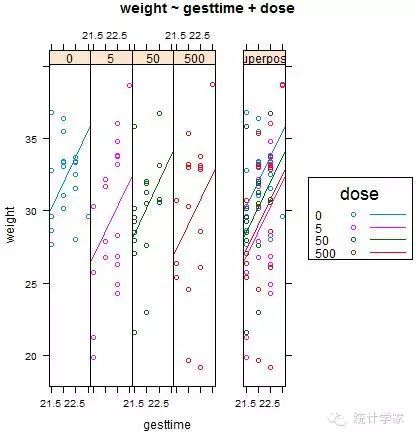
9.4.2 结果可视化
HH包中的ancova()函数可以绘制因变量、协变量和因子之间的关系图。
> library(HH)
> ancova(weight~gesttime+dose,data=litter)




 雷达卡
雷达卡








 京公网安备 11010802022788号
京公网安备 11010802022788号







