今天的内容是一期Python实战训练,我们来手把手教你用Python分析保险产品交叉销售和哪些因素有关。
01实战背景
首先介绍下实战的背景:
这次的数据集来自kaggle:
https://www.kaggle.com/anmolkumar/health-insurance-cross-sell-prediction
我们的客户是一家保险公司,最近新推出了一款汽车保险。现在他们的需要是建立一个模型,用来预测去年的投保人是否会对这款汽车保险感兴趣。
我们知道,保险单指的是,保险公司承诺为特定类型的损失、损害、疾病或死亡提供赔偿保证,客户则需要定期向保险公司支付一定的保险费。
这里再进一步说明一下。
例如,你每年要为20万的健康保险支付2000元的保险费。那么你肯定会想,保险公司只收取5000元的保费,这种情况下,怎么能承担如此高的住院费用呢? 这时,“概率”的概念就出现了。例如,像你一样,可能有100名客户每年支付2000元的保费,但当年住院的可能只有少数人,(比如2-3人),而不是所有人。通过这种方式,每个人都分担了其他人的风险。
和医疗保险一样,买了车险的话,每年都需要向保险公司支付一定数额的保险费,这样在车辆发生意外事故时,保险公司将向客户提供赔偿(称为“保险金额”)。

我们要做的就是建立模型,来预测客户是否对汽车保险感兴趣。这对保险公司来说是非常有帮助的,公司可以据此制定沟通策略,接触这些客户,并优化其商业模式和收入。
02数据理解
为了预测客户是否对车辆保险感兴趣,我们需要了解一些客户信息 (性别、年龄等)、车辆(车龄、损坏情况)、保单(保费、采购渠道)等信息。
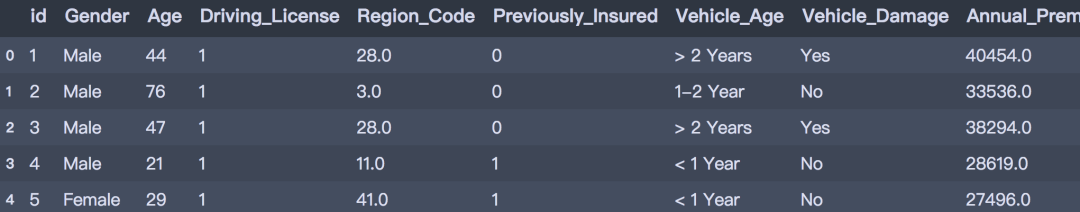
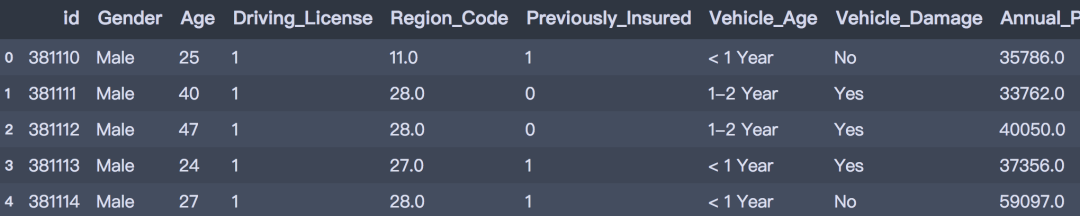
数据划分为训练集和测试集,训练数据包含381109笔客户资料,每笔客户资料包含12个字段,1个客户ID字段、10个输入字段及1个目标字段-Response是否响应(1代表感兴趣,0代表不感兴趣)。测试数据包含127037笔客户资料;字段个数与训练数据相同,目标字段没有值。字段的定义可参考下文。

下面我们开始吧!
03数据读入和预览
首先开始数据读入和预览。
- # 数据整理
- import numpy as np
- import pandas as pd
- # 可视化
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import seaborn as sns
- import plotly as py
- import plotly.graph_objs as go
- import plotly.express as px
- pyplot = py.offline.plot
- from exploratory_data_analysis import EDAnalysis # 自定义
- # 读入训练集
- train = pd.read_csv('../data/train.csv')
- train.head()
- # 读入测试集
- test = pd.read_csv('../data/test.csv')
- test.head()
- print(train.info())
- print('-' * 50)
- print(test.info())
- <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
- RangeIndex: 381109 entries, 0 to 381108
- Data columns (total 12 columns):
- # Column Non-Null Count Dtype
- --- ------ -------------- -----
- 0 id 381109 non-null int64
- 1 Gender 381109 non-null object
- 2 Age 381109 non-null int64
- 3 Driving_License 381109 non-null int64
- 4 Region_Code 381109 non-null float64
- 5 Previously_Insured 381109 non-null int64
- 6 Vehicle_Age 381109 non-null object
- 7 Vehicle_Damage 381109 non-null object
- 8 Annual_Premium 381109 non-null float64
- 9 Policy_Sales_Channel 381109 non-null float64
- 10 Vintage 381109 non-null int64
- 11 Response 381109 non-null int64
- dtypes: float64(3), int64(6), object(3)
- memory usage: 34.9+ MB
- None
- --------------------------------------------------
- <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
- RangeIndex: 127037 entries, 0 to 127036
- Data columns (total 11 columns):
- # Column Non-Null Count Dtype
- --- ------ -------------- -----
- 0 id 127037 non-null int64
- 1 Gender 127037 non-null object
- 2 Age 127037 non-null int64
- 3 Driving_License 127037 non-null int64
- 4 Region_Code 127037 non-null float64
- 5 Previously_Insured 127037 non-null int64
- 6 Vehicle_Age 127037 non-null object
- 7 Vehicle_Damage 127037 non-null object
- 8 Annual_Premium 127037 non-null float64
- 9 Policy_Sales_Channel 127037 non-null float64
- 10 Vintage 127037 non-null int64
- dtypes: float64(3), int64(5), object(3)
- memory usage: 10.7+ MB
- None
04探索性分析
下面,我们基于训练数据集进行探索性数据分析。
1. 描述性分析
首先对数据集中数值型属性进行描述性统计分析。
- desc_table = train.drop(['id', 'Vehicle_Age'], axis=1).describe().T
- desc_table
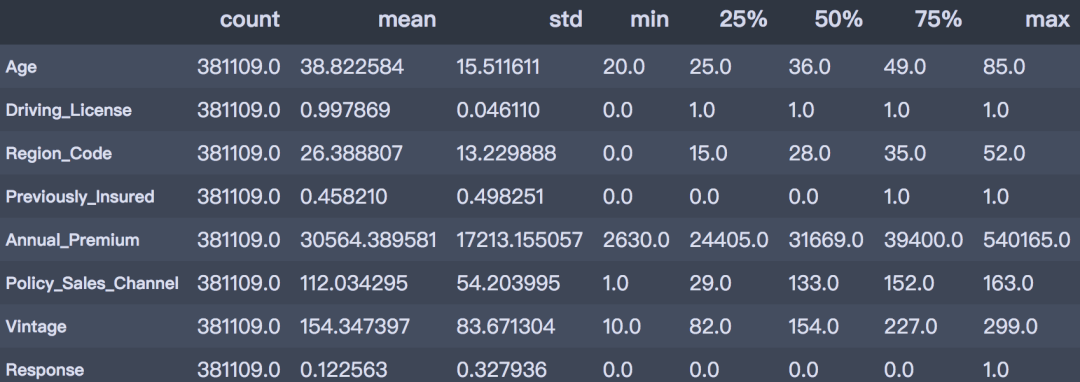
通过描述性分析后,可以得到以下结论。
从以上描述性分析结果可以得出:
- 客户年龄:客户的年龄范围在20 ~ 85岁之间,平均年龄是38岁,青年群体居多;
- 是否有驾照:99.89%客户都持有驾照;
- 之前是否投保:45.82%的客户已经购买了车辆保险;
- 年度保费:客户的保费范围在2630 ~ 540165之间,平均的保费金额是30564。
- 往来时长:此数据基于过去一年的数据,客户的往来时间范围在10~299天之间,平均往来时长为154天。
- 是否响应:平均来看,客户对车辆保险感兴趣的概率为12.25%。
2. 目标变量的分布
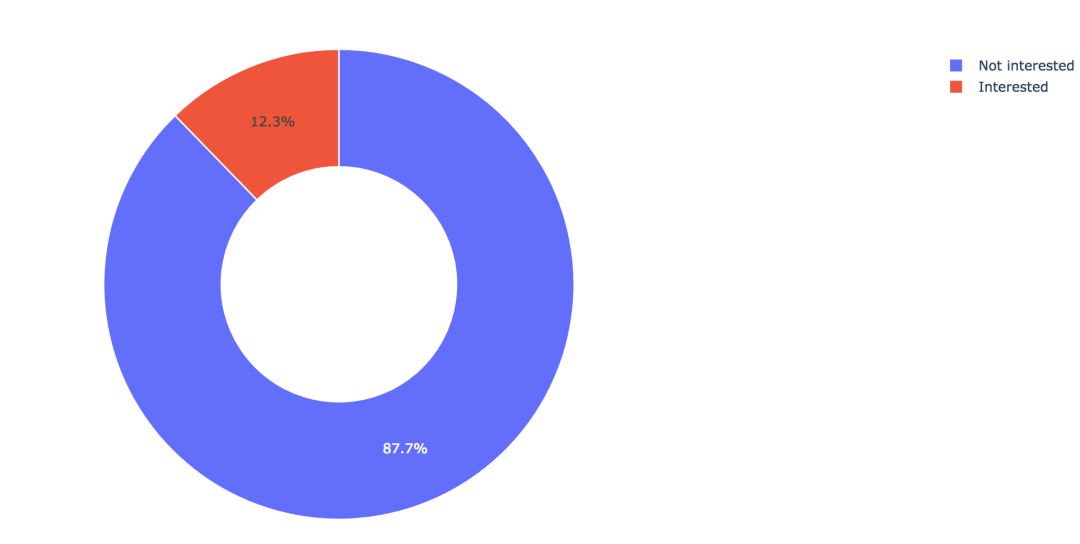
训练集共有381109笔客户资料,其中感兴趣的有46710人,占比12.3%,不感兴趣的有334399人,占比87.7%。
- train['Response'].value_counts()
- 0 334399
- 1 46710
- Name: Response, dtype: int64
- values = train['Response'].value_counts().values.tolist()
- # 轨迹
- trace1 = go.Pie(labels=['Not interested', 'Interested'],
- values=values,
- hole=.5,
- marker={'line': {'color': 'white', 'width': 1.3}}
- )
- # 轨迹列表
- data = [trace1]
- # 布局
- layout = go.Layout(title=f'Distribution_ratio of Response', height=600)
- # 画布
- fig = go.Figure(data=data, layout=layout)
- # 生成HTML
- pyplot(fig, filename='./html/目标变量分布.html')
3. 性别因素
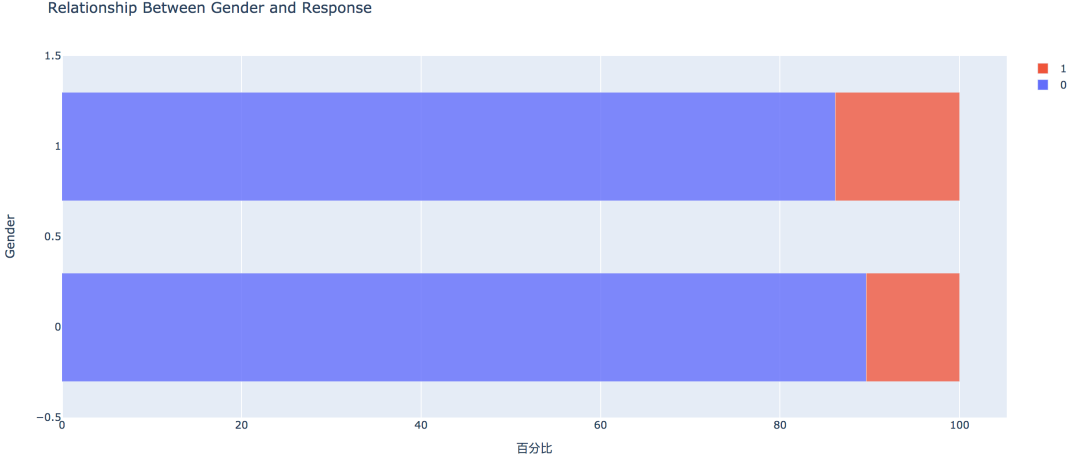
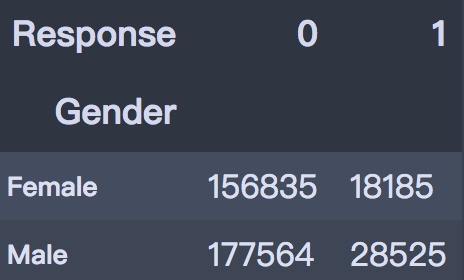
从条形图可以看出,男性的客户群体对汽车保险感兴趣的概率稍高,是13.84%,相较女性客户高出3个百分点。
- pd.crosstab(train['Gender'], train['Response'])
- # 实例类
- eda = EDAnalysis(data=train, id_col='id', target='Response')
- # 柱形图
- fig = eda.draw_bar_stack_cat(colname='Gender')
- pyplot(fig, filename='./html/性别与是否感兴趣.html')
4. 之前是否投保
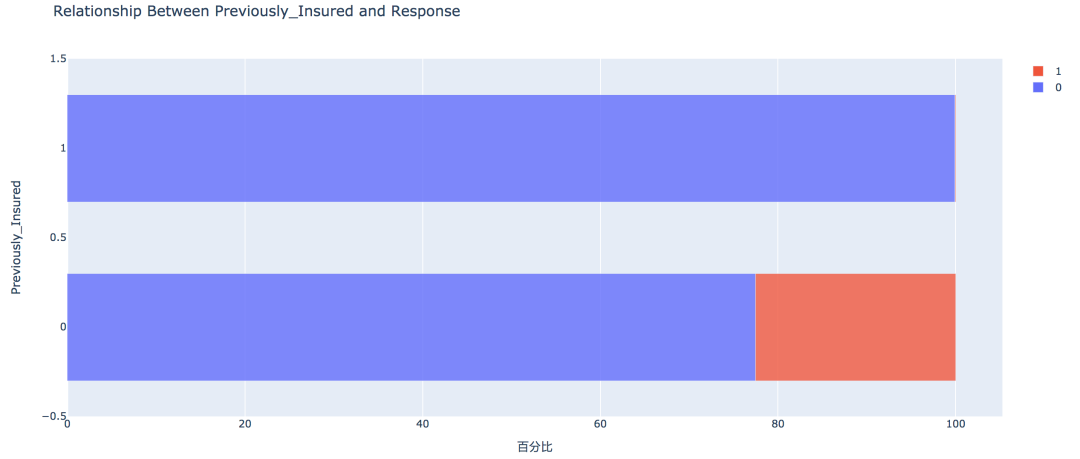
没有购买汽车保险的客户响应概率更高,为22.54%,有购买汽车保险的客户则没有这一需求,感兴趣的概率仅为0.09%。
- pd.crosstab(train['Previously_Insured'], train['Response'])

- fig = eda.draw_bar_stack_cat(colname='Previously_Insured')
- pyplot(fig, filename='./html/之前是否投保与是否感兴趣.html')
5. 车龄因素
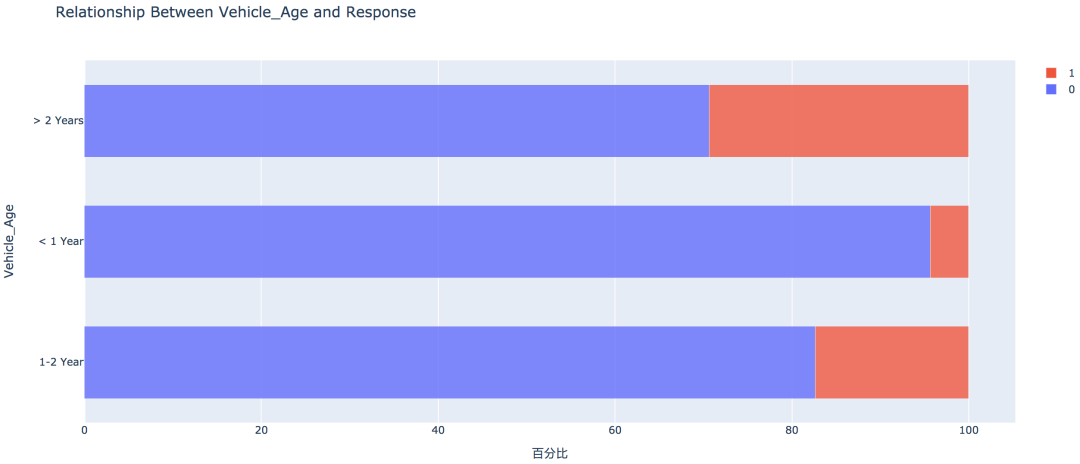
车龄越大,响应概率越高,大于两年的车龄感兴趣的概率最高,为29.37%,其次是1~2年车龄,概率为17.38%。小于1年的仅为4.37%。
6. 车辆损坏情况
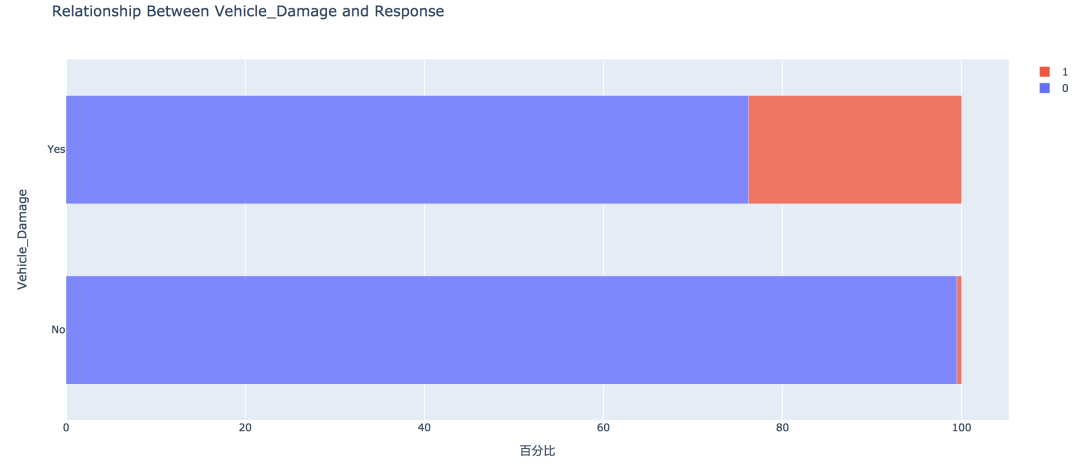
车辆曾经损坏过的客户有较高的响应概率,为23.76%,相比之下,客户过去车辆没有损坏的响应概率仅为0.52%
7. 不同年龄
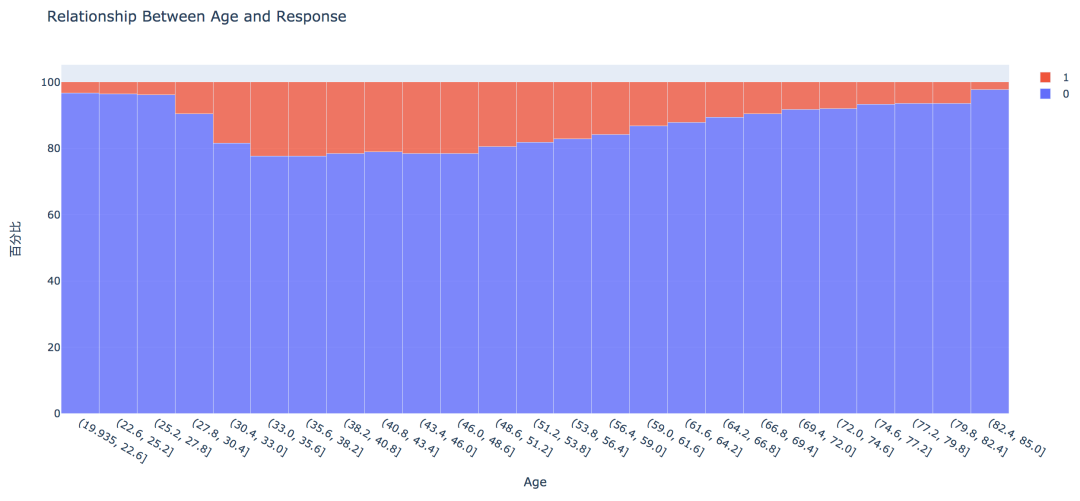
从直方图中可以看出,年龄较高的群体和较低的群体响应的概率较低,30~60岁之前的客户响应概率较高。
通过可视化探索,我们大致可以知道:
车龄在1年以上,之前有车辆损坏的情况出现,且未购买过车辆保险的客户有较高的响应概率。
05数据预处理
此部分工作主要包含字段选择,数据清洗和数据编码,字段的处理如下:
- Region_Code和Policy_Sales_Channel:分类数过多,且不易解读,删除;
- Annual_Premium:异常值处理
- Gender、Vehicle_Age、Vehicle_Damage:分类型数据转换为数值型编码
- # 删除字段
- train = train.drop(['Region_Code', 'Policy_Sales_Channel'], axis=1)
- # 盖帽法处理异常值
- f_max = train['Annual_Premium'].mean() + 3*train['Annual_Premium'].std()
- f_min = train['Annual_Premium'].mean() - 3*train['Annual_Premium'].std()
- train.loc[train['Annual_Premium'] > f_max, 'Annual_Premium'] = f_max
- train.loc[train['Annual_Premium'] < f_min, 'Annual_Premium'] = f_min
- # 数据编码
- train['Gender'] = train['Gender'].map({'Male': 1, 'Female': 0})
- train['Vehicle_Damage'] = train['Vehicle_Damage'].map({'Yes': 1, 'No': 0})
- train['Vehicle_Age'] = train['Vehicle_Age'].map({'< 1 Year': 0, '1-2 Year': 1, '> 2 Years': 2})
- train.head()
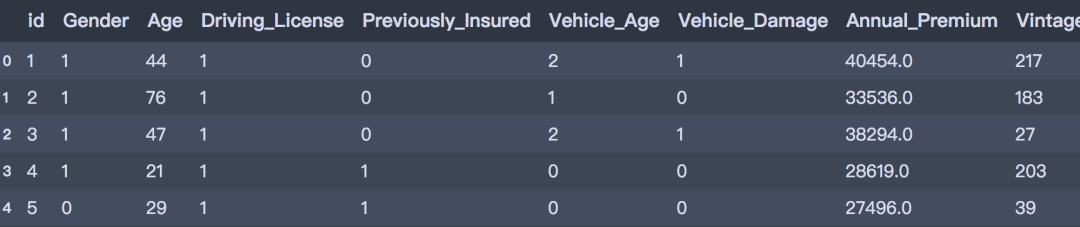
测试集做相同的处理:
- # 删除字段
- test = test.drop(['Region_Code', 'Policy_Sales_Channel'], axis=1)
- # 盖帽法处理
- test.loc[test['Annual_Premium'] > f_max, 'Annual_Premium'] = f_max
- test.loc[test['Annual_Premium'] < f_min, 'Annual_Premium'] = f_min
- # 数据编码
- test['Gender'] = test['Gender'].map({'Male': 1, 'Female': 0})
- test['Vehicle_Damage'] = test['Vehicle_Damage'].map({'Yes': 1, 'No': 0})
- test['Vehicle_Age'] = test['Vehicle_Age'].map({'< 1 Year': 0, '1-2 Year': 1, '> 2 Years': 2})
- test.head()
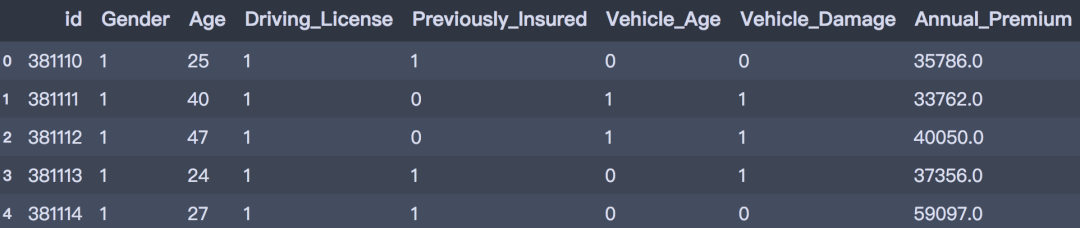
06数据建模
我们选择使用以下几种模型进行建置,并比较模型的分类效能。
首先在将训练集划分为训练集和验证集,其中训练集用于训练模型,验证集用于验证模型效果。首先导入建模库:
- # 建模
- from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
- from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
- from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
- from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
- from lightgbm import LGBMClassifier
- # 预处理
- from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler, MinMaxScaler
- # 模型评估
- from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, GridSearchCV
- from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report, accuracy_score, f1_score, roc_auc_score
- # 划分特征和标签
- X = train.drop(['id', 'Response'], axis=1)
- y = train['Response']
- # 划分训练集和验证集(分层抽样)
- X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, stratify=y, random_state=0)
- print(X_train.shape, X_val.shape, y_train.shape, y_val.shape)
- (304887, 8) (76222, 8) (304887,) (76222,)
- # 处理样本不平衡,对0类样本进行降采样
- from imblearn.under_sampling import RandomUnderSampler
- under_model = RandomUnderSampler(sampling_strategy={0:133759, 1:37368}, random_state=0)
- X_train, y_train = under_model.fit_sample(X_train, y_train)
- # 保存一份极值标准化的数据
- mms = MinMaxScaler()
- X_train_scaled = pd.DataFrame(mms.fit_transform(X_train), columns=x_under.columns)
- X_val_scaled = pd.DataFrame(mms.transform(X_val), columns=x_under.columns)
- # 测试集
- X_test = test.drop('id', axis=1)
- X_test_scaled = pd.DataFrame(mms.transform(X_test), columns=X_test.columns)
1. KNN算法
- # 建立knn
- knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3, n_jobs=-1)
- knn.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)
- y_pred = knn.predict(X_val_scaled)
- print('Simple KNeighborsClassifier accuracy:%.3f' % (accuracy_score(y_val, y_pred)))
- print('Simple KNeighborsClassifier f1_score: %.3f' % (f1_score(y_val, y_pred)))
- print('Simple KNeighborsClassifier roc_auc_score: %.3f' % (roc_auc_score(y_val, y_pred)))
- Simple KNeighborsClassifier accuracy:0.807
- Simple KNeighborsClassifier f1_score: 0.337
- Simple KNeighborsClassifier roc_auc_score: 0.632
- # 对测试集评估
- test_y = knn.predict(X_test_scaled)
- test_y[:5]
- array([0, 0, 1, 0, 0], dtype=int64)
2. Logistic回归
- # Logistic回归
- lr = LogisticRegression()
- lr.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)
- y_pred = lr.predict(X_val_scaled)
- print('Simple LogisticRegression accuracy:%.3f' % (accuracy_score(y_val, y_pred)))
- print('Simple LogisticRegression f1_score: %.3f' % (f1_score(y_val, y_pred)))
- print('Simple LogisticRegression roc_auc_score: %.3f' % (roc_auc_score(y_val, y_pred)))
- Simple LogisticRegression accuracy:0.863
- Simple LogisticRegression f1_score: 0.156
- Simple LogisticRegression roc_auc_score: 0.536
3. 决策树
- # 决策树
- dtc = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=10, random_state=0)
- dtc.fit(X_train, y_train)
- y_pred = dtc.predict(X_val)
- print('Simple DecisionTreeClassifier accuracy:%.3f' % (accuracy_score(y_val, y_pred)))
- print('Simple DecisionTreeClassifier f1_score: %.3f' % (f1_score(y_val, y_pred)))
- print('Simple DecisionTreeClassifier roc_auc_score: %.3f' % (roc_auc_score(y_val, y_pred)))
- Simple DecisionTreeClassifier accuracy:0.849
- Simple DecisionTreeClassifier f1_score: 0.310
- Simple DecisionTreeClassifier roc_auc_score: 0.603
4. 随机森林
- # 决策树
- rfc = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, max_depth=10, n_jobs=-1)
- rfc.fit(X_train, y_train)
- y_pred = rfc.predict(X_val)
- print('Simple RandomForestClassifier accuracy:%.3f' % (accuracy_score(y_val, y_pred)))
- print('Simple RandomForestClassifier f1_score: %.3f' % (f1_score(y_val, y_pred)))
- print('Simple RandomForestClassifier roc_auc_score: %.3f' % (roc_auc_score(y_val, y_pred)))
- Simple RandomForestClassifier accuracy:0.870
- Simple RandomForestClassifier f1_score: 0.177
- Simple RandomForestClassifier roc_auc_score: 0.545
5. LightGBM
- lgbm = LGBMClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=0)
- lgbm.fit(X_train, y_train)
- y_pred = lgbm.predict(X_val)
- print('Simple LGBM accuracy: %.3f' % (accuracy_score(y_val, y_pred)))
- print('Simple LGBM f1_score: %.3f' % (f1_score(y_val, y_pred)))
- print('Simple LGBM roc_auc_score: %.3f' % (roc_auc_score(y_val, y_pred)))
- Simple LGBM accuracy: 0.857
- Simple LGBM f1_score: 0.290
- Simple LGBM roc_auc_score: 0.591
综上,以f1-score作为评价标准的情况下,KNN算法有较好的分类效能,这可能是由于数据样本本身不平衡导致,后续可以通过其他类别不平衡的方式做进一步处理,同时可以通过参数调整的方式来优化其他模型,通过调整预测的门槛值来增加预测效能等其他方式。
相关帖子DA内容精选
|




 雷达卡
雷达卡









 京公网安备 11010802022788号
京公网安备 11010802022788号







